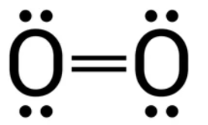Explain the formation of O2molecules using molecular orbital theory.
A molecular orbital (or MO) is an orbital in the atomic structure of molecules. It is a molecule’s electron wave function that is used to calculate its chemical and physical properties.
Molecular orbital diagram of oxygen molecule:
Given element – Oxygen
Atomic number of oxygen – 8
Electronic configuration – 1s²2s²2p4
Total number of electrons in nitrogen molecule – 16
Molecular orbital diagram of O2 is as follows;
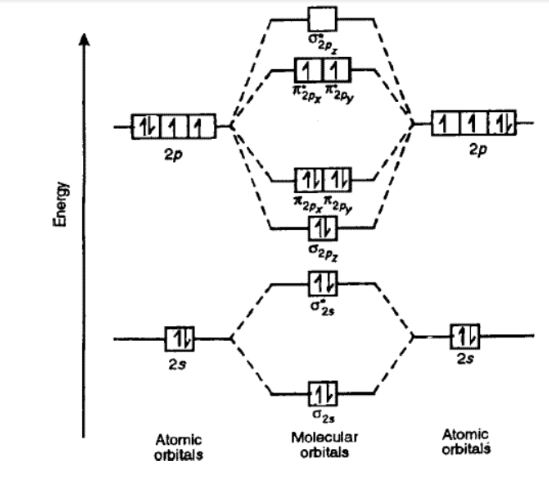
Electronic configuration of oxygen molecule;
ó1s² < *ó1s² < ó2s² < *ó2s² , [ π2px² = π2py²] < ó 2pz² < [*π2px¹ =*π2py¹] < *ó2pz
Let’ s calculate the bond order of O;
Bond order = Bonding electrons – Anti bonding electrons / 2
= 10 – 6 / 2 = 2
Thereofore, the order of O2 is 2.
O2 have unpaired electrons, Hence it is Paramagnetic.
The structure of O2 is as follows;
 Profile
Profile Settings
Settings Refer your friends
Refer your friends Sign out
Sign out