Answer: Functional groups are unique groups of atoms within molecules that are responsible for the molecules’ characteristic chemical reactions in organic chemistry. They are less stable than the carbon backbone and are more prone to participate in chemical processes.
To know about aliphatic and aromatic functional groups first we need to learn about the hydrocarbons that make these functional groups aliphatic and aromatic in nature.
1. Aliphatic hydrocarbons: These are organic molecules that contain carbon and hydrogen atoms in straight, branching, or non-aromatic ring structures. Covalent bonds are formed between carbon and hydrogen atoms. Alkanes, alkenes, and alkynes are three forms of aliphatic hydrocarbons.
The majority of aliphatic hydrocarbons are combustible. Aliphatic hydrocarbons can also be classified as cyclic molecules. This is due to the non-aromatic nature of those cyclic structures.
2. Aromatic hydrocarbons: These are organic compounds with delocalized pi-electrons that are made up of carbon and hydrogen atoms organized in ring configurations. Aromatic hydrocarbons get their name from their pleasant odor. Aromatic rings that get attached to a functional group have the structure as shown in the figure below,
![]() Hence, the differences between aliphatic and aromatic functional groups are:
Hence, the differences between aliphatic and aromatic functional groups are:
Examples of Aliphatic functional groups
![]()
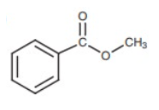
![]() Examples of Aromatic functional groups
Examples of Aromatic functional groups
![]()
![]()
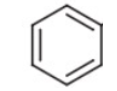 Hence, the differences between aliphatic and aromatic functional groups are:
Hence, the differences between aliphatic and aromatic functional groups are:
| Aliphatic Functional groups | Aromatic Functional groups |
| 1. If there is no aromatic ring immediately connected to a functional group, it is classified as aliphatic. | 1. If a functional group has an aromatic ring immediately linked to it, it is classified as aromatic. |
| 2. If the aromatic ring is not directly linked to the functional group, an aromatic molecule with an aliphatic functional group is feasible. | 2. The functional groups are defined as aliphatic when the aromatic ring is connected to the heteroatom. |
| 3. It exhibits all properties of aliphatic hydrocarbons such as combustion. | 3. It exhibits all properties of aromatic hydrocarbons such as electrophilic substitution. |
- Aliphatic Ketone
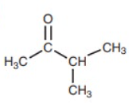
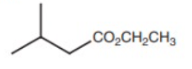
- Aliphatic Ester
 Examples of Aromatic functional groups
Examples of Aromatic functional groups
- Aromatic Amide
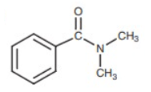
- Aromatic ester
 Profile
Profile Settings
Settings Refer your friends
Refer your friends Sign out
Sign out






