How to Calculate Valency of Nitrate?
Valency refers to the number of electrons that are gained or lost by an atom in order to complete its outermost shell. By completing their outer shell, or octet (8 electrons in the outmost shell), the atoms become stable.
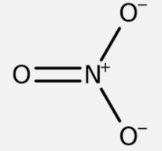
Nitrate has the chemical formula NO3- which makes it a nitrogen-oxygen compound. Nitrate is a naturally occurring chemical created when nitrogen reacts with oxygen or ozone. Although all living things require nitrogen, large quantities of nitrate in drinking water can be harmful to health, especially for infants and pregnant women. The structure of the chemical bonding of nitrate is:
The octet rule is used to determine the valency of a chemical formula, and the valency can be determined by looking at how an element is combined.
Now, the valency of nitrate NO3– has three oxygen atoms and one nitrogen atom. Nitrogen is a member of the periodic table’s group -15, and it forms bonds with three oxygen atoms with a charge of +5. Oxygen has a valency of -2 because it belongs to the periodic table’s group – 16.
As a result, the valency of the nitrate ion is
=5-[3×2]
=5-6
=-1
Thus, the valency of nitrate NO3– is -1.
Some applications of different compounds of nitrates are:
- In numerous forms of fireworks, sodium nitrate is employed as an oxidizer.
- Some rapid cold packs contain it as well.
- Because of their great solubility and biodegradability, nitrates are primarily generated for use as fertilisers in agriculture.
- Nitrates are vasodilators (blood vessel dilation) that are used to treat angina (chest pain caused by a shortage of oxygen to the heart muscle) and congestive heart failure symptoms.
- Potassium nitrate is used in toothpaste to make teeth less sensitive to pain.
- In the food business, it’s used to keep meat safe from microbiological pathogens.
 Profile
Profile Settings
Settings Refer your friends
Refer your friends Sign out
Sign out