The total number of moles of solute per litre of solution is known as the molarity of a solution.
where,
M= The molality of a solution,
n= number of moles of a solute is n.
V= the volume of the solution in litres.
Using the formula of molarity, we can calculate the number of moles in oxalic acid (H2C2O4.2H2O)
As we know, the molar mass of oxalic acid (H2C2O4.2H2O) = 126 g/mol.
Using,
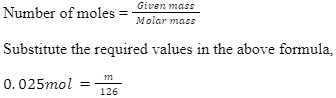
m=3.15g
Thus, the mass of oxalic acid (H2C2O4.2H2O) needed to prepare 250 ml,1 M aqueous solution of oxalic acid is 3.15 grams.