Several methods are used to determine the various properties of electrochemical reactions; one such method is cyclic voltammetry, or the CV method. This method provides a calculation for currents in electrochemical cells.
The produced data from the analysis can be plotted on a graph; this provides an s-shape curve, or a duck-shaped curve. It is called the c-v curve, or cyclic voltammogram. In the following article, we will learn about cyclic voltammetry, the origin of the s-shaped c v curve, and the various properties of cyclic voltammogram.
Electrochemical Cell
The electrochemical cell is a mechanism that uses redox reactions to generate electricity in a system.
An electrochemical cell is composed of two conductive electrodes, called cathode and anode. Oxidation reaction occurs at the anode, and reduction reactions occur at the cathode.
Cyclic Voltammetry
Cyclic voltammetry, or simply CV, is defined as an electrochemical process of measuring the qualitative properties of the electrochemical reactions. This method is used in calculating the currents in electrochemical cells, given that the voltage in the circuit between two points is in excess of the Nernst Equation.
The cyclic voltammetry method is one of the most followed methods to determine the thermodynamics of redox processes, the energy levels in analytes, and the kinetics of electronic-transfer reactions.
Working on Cyclic Voltammetry
Cyclic voltammetry uses a three-electrode system; this system consists of the following,
- Working electrode
- Counter Electrode
- Reference Electrode
The working procedure and origin of the s-shaped c v curve of Cyclic Voltammetry follow the following steps:
- In the first step, the given electrolyte solution is added to the electrochemical cell in the first step.
- A reference solution and three electrodes are added to the electrochemical cell, along with the electrolyte solution.
- To linearly sweep the electric potential between the working electrode and reference electrodes, a potentiostat is used in the electrochemical cell.
- The potentiostat is used until it reaches the pre-set limit.
- After potentiostat reaches the pre-set limit, it is swept back in the opposite direction.
- The same process is repeated many times.
- The changing current is continuously measured.
Cyclic voltammetry results are presented on a duck-shaped or s-shaped curve; this gives a c-v curve or cyclic voltammogram.
Cyclic Voltammetry Curve
A cyclic voltammetry curve is an s-shaped curve (duck-shaped curve). It is also called a c-v curve, or Cyclic voltammogram.
A cyclic voltammogram, or a c-v curve, is obtained by measuring the electric current at the working electrodes during the cyclic potential scans.
Understanding the C-V Curve
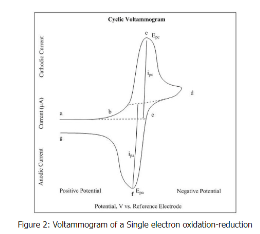
To understand the origin of the s-shaped c v curve, let us look at the following example of a reversible reaction,
M+ + e− ⇌ M
- In the above c-v curve, the reduction process occurs from point a to d, where a is the initial point, and d is the switching potential.
- In the region from a to d, the potential is measured in -ve values to cause a reduction.
- The resulting current due to points a and d in the system is called cathodic current.
- The peak potential is achieved at point c.
- The peak potential is called the cathodic potential.
- When the switching potential point is reached, the scans from point d to g.
- This scan is done in +ve values.
- This scan results in the anodic current in the system.
- The peak potential is achieved at point f.
- This is called anodic peak potential.
The details mentioned above can be understood by observing the s-shaped curve in a cyclic voltammogram.
Instrumentation Required for Cyclic Voltammetry
The following instruments are used in cyclic voltammetry,
- Electrolysis cells
- Potentiostats
- A current-to-voltage convertor
- A data acquisition system
The electrochemical cell consists of the following instruments,
- Working electrode
- Reference Electrode
- Counter Electrode
- Electrolytic Solution
Applications of Cyclic Voltammetry
Cyclic voltammetry has a wide range of applications in electrochemical processes; some of the important applications of this method are given below:
- The cyclic voltammetry method can be used for understanding and analysing various electrochemical processes under different environments and conditions.
- Some of the electrochemical process applications include analysis of intermediates in oxidation-reduction reactions, and the reversibility of a reaction.
- The c-v curve can also be used to determine the electron stoichiometry of a system.
- The diffusion coefficient of an analyte can be determined using the c-v curve.
- The formal reduction potential of a system can also be determined using a c-v curve. The c-v curve can determine even the concentration of an unknown solution.
Conclusion
Cyclic voltammetry is used to determine the properties of electrochemical reactions; this method is used to determine the current between two points in a Nernst equation. The electrochemical cell is used to determine the cyclic voltammogram; the cyclic voltammogram gives an s-shaped curve, which provides various electrochemical properties of the system.
Electrodes are the main instrument in cyclic voltammetry. The applications of cyclic voltammetry have varied implications; this method can be used to determine various other properties by the c-v curve.
 Profile
Profile Settings
Settings Refer your friends
Refer your friends Sign out
Sign out