Pharmaceutical is a professional field that connects medical sciences and chemistry. It is also responsible for producing, disposing of, effectively, controlling and using drugs. Potentiometry is very important in this field. The scientist Nernst proposed an equation that shows that the potential of an electrochemical cell is proportional to the concentration of a sample. This happened in the year 1889. Cremer discovered that a potential difference persists between reference and indicator electrodes in the year 1906. The main aim of potentiometry is to find out the electromotive force of a solution sample. This is achieved by using a galvanic cell. The next section will discuss potentiometry and pharmaceutical analysis.
Potentiometry and Pharmaceutical Analysis
The Principle of Potentiometry
When a pair of electrodes are put in a solution sample, it determines the difference in potential. This is recorded after adding a titrant or by when there is an alteration of the concentration of ions. The potential difference of a full (complete) cell is given by this equation: Ecell = -Eref + Eindicator + Ejunction
Here, Eref denotes the potential difference of the reference electrode
Eindicator denotes the potential difference of the indicator electrode
Ejunction denoted the potential difference at the junction of the sample solution. The cell potential is measured in mV (millivolts)
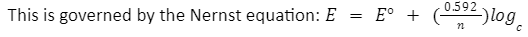
Here, E denotes the solution potential
E° denotes the standard potential of the electrode
n denotes the valency of the ion in the sample solution
c denotes the concentration of the solution sample.
The mechanism that takes place here is
- The electrons travel from the reference electrode to the indicator electrode.
- The negative ions (anions) migrate to the anode
- The positive ions travel (cations) to the cathode
Pharmaceutical analysis is described as a series of processes that involves identifying, determining, and purifying a compound. It is utilised in the formulation of a pharmaceutical product. There are various samples analysed in the pharmaceutical analysis. They are – finished pharmaceutical products, biological samples, and pharmaceutical raw materials. It can be done by many analytic methods, and one such method is called potentiometric titration.
What is Potentiometric Titration in Pharmaceutical Analysis?
The Principle of Potentiometric Titration
The endpoint is measured when there is a sudden change in the electric potential. This happens when a titrant is added to the solution sample. This happens because there is an alternation in the ionic activity and concentration of the solution sample. There are three elements in a basic potentiometric titration. They are – a reference electrode, an indicator electrode, and a mechanical stirrer. The endpoint is deter
mined when there is a rapid change in the solution potential. An electronic voltmeter is used to determine the electromotive force of the solution sample.
There are four types of potentiometric titrations in pharmaceutical analysis. They are
Complexometric Titration
This titration is achieved by an electrode of a metal whose ions are involved in complex formation. For example, silver electrodes are used to titrate cyanide ions with a standard silver solution. The complex formation reaction is Ag++ 2CN- ⇋ [Ag(CN)2-]
Ag(CN)2 forms a solid precipitate after reaching the equivalence point. After this point, adding silver does not change the concentration of the complex. If more than one complex is formed, this reaction becomes complicated. In this situation, EDTA can be used to handle.
Acid-base Titration
There is a change in concentrations of H+ and OH- during the neutralisation of bases and acids. A hydrogen electrode is used in this titration. The reference electrode is the N-Calomel electrode (NCE).
An acid of known volume is kept in a beaker with an automatic stirrer. The hydrogen electrode is linked to NCE through a salt bridge. The hydrogen and NCE are connected to a potentiometer which tracks the EMF (electromotive force).
Precipitation Titration
An indicator electrode is made of a metal that is involved in the reaction. The other type of electrode that can be used is whose potential is governed by the anion concentration that is being precipitated. The endpoint magnitude is determined by the solubility of the substance that is being precipitated.
Oxidation-reduction Titration
This titration uses an indicator electrode. This electrode presumes a potential that is proportional to the logarithm of the concentration of the two oxidation states (reactant or titrant).
Importance of Potentiometric Titration in Pharmaceutical Analysis
The importance of potentiometric titrations in the pharmaceutical analysis are
- This type of titration does not require an indicator electrode. But there are a few potentiometric titrations with both reference and indicator electrodes.
- This titration is very accurate and gives precise results up to three digits in millimetres.
- Depending on the determining analytes, there are several potentiometric titrations. They are – redox, acid-base, complexometric, and precipitation titrations.
- This titration works almost as well as automated systems along with a great capacity for processing samples.
- The modern methods of this titration can be used to find out pH, like HPLC (high-performance liquid chromatography)
- It is affordable and simple. Hence, can be used widely.
Conclusion
This article talks about potentiometry and pharmaceutical analysis. Potentiometry is used to find out the electromotive force of a solution sample. The potential of a full cell is determined by Ecell = -Eref + Eindicator + Ejunction. It is governed by the Nernst equation
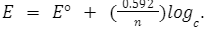
The series of processes like purifying, identifying, and determining a compound that is used to formulate pharmaceutical drugs is called pharmaceutical analysis. Potentiometric titration is a method used in pharmaceutical analysis. There are four types of potentiometric titrations – complexometric, acid-base, oxidation-reduction, and precipitation. This article also discussed the importance of potentiometric titrations in pharmaceutical analysis.
 Profile
Profile Settings
Settings Refer your friends
Refer your friends Sign out
Sign out






