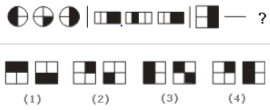
Visual reasoning is the ability to analyse, process, and manipulate visual information to solve problems. The information in graphs, charts, and maps requires a combination of word, mathematical, and visual analysis to interpret the information accurately.
To answer these situation-based questions, the candidate is asked to identify and manipulate visual objects in different situations.
One’s ability to understand visual-based problems shows the sharpness and grasping power of the mind. Simple Methods to Solve Visual Reasoning Questions enables you to analyse and crack difficult questions without trusting language skills.
These problems are in the form of figures, drawings and designs, series, analogies, classification, cube turning, mirror image, paper folding, paper cutting, completion of the incomplete pattern, figure perception, spotting the hidden designs, or construction of squares.
Rules
Some rules and Simple Methods to Solve Visual Reasoning Questions are as follows:
- Answering the questions of visual reasoning is not necessary and doesn’t require either written or spoken solutions. The answer is derived by analysing the visual image and graphic pattern.
- Based on the 4-5 images that are provided in the questions in the abstract conceptual reasoning, you must choose the figure from the choices given to you.
- In the case of the analogy type questions, three figures are given to you, and you have to locate the fourth figure that shares a similarity with the figure. The relationship must be similar to the figure and that of the previous figure.
- It is important to determine what the paper will look like after folding it.
- If you are asked to answer questions with figures embedded, it is necessary to select an option in which the figure in question is embedded, or embedded with the help of additional figures, lines, or other images.
Examples and Solved Visual Reasoning Questions and Answers
Here are some commonly asked different types of visual problems.
Analogies
Analogies have two figures, the problem figures, and the answer figures. You have to establish a relationship between two figures and point out which one of the answer figures should be in place of the question mark.
Example: 1
Consider the below problem figures.
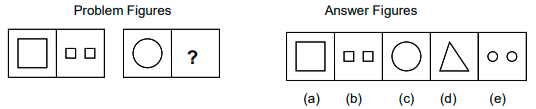
The second figure is related to the first figure in a certain way. The elements in the second figure are double the elements in the first figure. The first figure has one square, and the second has two squares. The third and fourth figures should also have the same relationship as the first and second have. That means that the fourth figure should have two circles.
∴The answer is (e).
EXAMPLE 2.
Look carefully at the sequence of symbols to find the pattern. Select the correct pattern.
(a) 1
(b) 2
(c) 3
(d) 4
Sol: Option D
Explanation: The figures alternate between one-half and one-fourth shaded in each segment.
Series
The four figures given on the left are the problem figures. The following five are the answer figures. The problem figures make up a series. That means they change from left to right in a specific order.
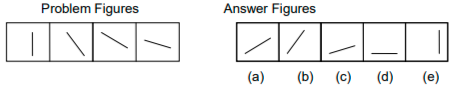
Example 3:
The line across the problem figures is falling. Thus, if the line continues to fall, its fifth position would lie flat, i.e., horizontal. Therefore the answer is (d).
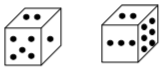
Problems with Dice
Sometimes, figures are given showing the same dice in various positions. One has to find the number opposite a given number on the dice. The procedure for finding such a number will be clear from the example below.
Example 5:
Two positions of a block are given below. When is one at the top, and which number will be at the bottom?
In both figures, 2 is at the top. To get the position of the second figure, we have to rotate the dice in the first figure two times in a clockwise direction. After rotating the dice two times in the same direction, 6 comes in the place of 1. So 6 is on the side opposite the 1. ∴
The answer is (b).
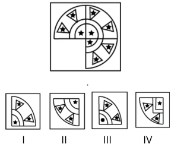
Completion of Pattern
In this type of problem, we have to find out the missing part of the figure.
Example: 6
Among the given options, which figure will complete the question figure?
- I
- II
- III
- IV
Answer: Option II
Explanation: We need the bottom left of the quadrant to complete the question figure, So Option II satisfies the criteria.
Key Points to Remember When Attempting to Solve Visual Reasoning Questions to Improve Visual Reasoning Problems
Here are some suggestions to help students improve their visual reasoning skills:
- Pay attention to information that is visual and imagery. Visualisation can help students visualise objects that are not physically in the present. It is an essential capability in spatial reasoning as well as solving problems.
- Be aware of how you understand and process visual information.
- Make use of your strong verbal skills to communicate visual pattern challenges.
- It encourages students to link spatial relationships and the objects that surround them. The use of spatial terms can help students to be more effective in activities of spatial reasoning. Start this process as early as the child’s development by asking, “Is that candy in or out of the wrapper?”
- Introduce games that improve children’s spatial abilities, such as Jigsaw puzzles, Tangram (Chinese puzzles comprising seven pieces) or building blocks.
Conclusion
Visual reasoning assists students in solving problems through analysing, processing, or manipulating information from visual sources. The ability to mentally remember the location of patterns and objects helps students to learn Simple Strategies to Solve Visual Reasoning questions. Offering children the chance to develop their spatial awareness is essential in the classroom. It aids them in managing their day-to-day activities and assists them in remembering key points to keep in mind when they are trying to answer problems involving visual reasoning. In daily life, the ability to see is essential. A variety of careers and occupations require this ability. If you are looking for a simple task, like packing bags for your trip, you must know the places items should go to maximise storage space.
 Profile
Profile Settings
Settings Refer your friends
Refer your friends Sign out
Sign out