The Willgerodt-Kindler Reaction is an organic synthesis reaction that involves the coupling of aryl halides with aldehydes. Named after Fritz Willgerodt and Theodor Kindler, who published their findings in 1954, this reaction was used to produce various molecules, including pharmaceuticals, fragrances, dyes, and other speciality chemicals. The reaction occurs under acidic conditions in the presence of a palladium catalyst and typically proceeds with high yields. Named after its discoverers, the response is used in organic chemistry to produce imines from aldehydes and amines. The reaction product is a Schiff base, which converts into various other products depending on the reactants.
Steps of the Willgerodt-Kindler Reaction?
From aldehydes and nitriles, the Willgerodt-Kindler Reaction produces ketones. The reaction begins with forming an imine, which is then hydrolysed to create the desired ketone. The response is a reliable and efficient way to produce ketones and can be performed in various solvents.
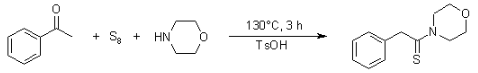
The Willgerodt-Kindler Reaction is a sequence of organic reactions that produce an aldehyde from alcohol. The steps of the response are as follows:
- The alcohol is converted into an aldehyde with the help of a dehydrogenase enzyme.
- The aldehyde is then converted into an acid chloride with the help of a thionyl chloride molecule.
- The acid chloride is then converted into an ester with the help of alcohol.
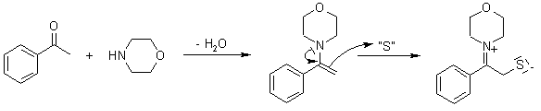
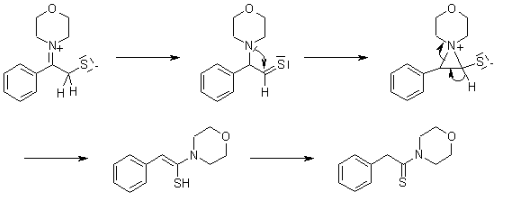
Benefits of using the Willgerodt-Kindler Reaction
The Willgerodt-Kindler reaction is a synthetic organic reaction that produces an aryl ketone from an aryl halide and an alkene. This reaction was developed by Willgerodt and Kindler in 1937 and has been widely used to synthesise pharmaceuticals, agrochemicals, and other fine chemicals. The benefits of using this reaction include:
- It is a versatile reaction used to synthesise a wide variety of products.
- It is efficient and produces high yields of products.
- It is reliable and is used to manufacture many products.
The Willgerodt-Kindler reaction is a powerful tool for the synthesis of carbon-carbon bonds. When used in the presence of an organocatalyst, it can produce functionalized ketones and aldehydes in high yield. The reaction is simple to execute, and the products are typically stable and easy to purify.
Drawbacks of using the Willgerodt-Kindler Reaction
The Willgerodt-Kindler Reaction is a process used to synthesise certain types of compounds. However, there are some drawbacks to using this reaction:
- The process is very long, making it difficult to produce large quantities of the desired compound. Additionally, the reaction can be unpredictable, meaning that it is not always possible to achieve the desired result.
- The Willgerodt-Kindler reaction often produces racemic mixtures. This demerit means that the product contains two mirror-image versions of the molecule, and it is impossible to determine which one is the desired product.
- The reaction requires a strong base, which can be challenging to control. If the base is too strong, it can react with the alcohol and produce water, which will halt the reaction. If the base is too weak, the response will not proceed efficiently. It is not always possible to create the desired outcome.
- This reaction can be dangerous if not performed correctly. It can release harmful fumes and produce hazardous byproducts.
How can you perform the Willgerodt-Kindler reaction?
The Willgerodt-Kindler reaction modifies the Perkin reaction that produces α and β-unsaturated ketones. The Willgerodt-Kindler reaction uses an aryl halide, an aryl Grignard reagent, and an aldehyde in the presence of a base to produce the desired product. The key to this reaction is the use of an aryl Grignard reagent. Magnesium reacts with an aryl halide to form this reagent. The aryl halide is then added to the aldehyde in the presence of a base to form the aryl Grignard reagent.
This reaction forms an iminium ion which is then converted to the ketone. The key to this reaction is the use of an aryl Grignard reagent.
Conclusion
This article looks at the Willgerodt-Kindler reaction, a chemical reaction to produce ketones. The Willgerodt-Kindler reaction is a type of organic reaction that forms an aldehyde from two ketones, and it is a Claisen condensation and can be used to form carbon-carbon bonds. The reaction is named for its discoverers, Hans Willgerodt and Heinrich Kindler. The article provides a detailed description of the reaction, including the steps involved and the produced products. To learn more about the Willgerodt-Kindler reaction, visit our website.
 Profile
Profile Settings
Settings Refer your friends
Refer your friends Sign out
Sign out






