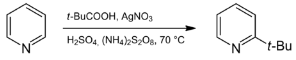
The miniaturised chemical sciences, or minisci, hold great potential to revolutionise drug discovery, materials science, and other areas. The three-component minisci reaction is one powerful tool that enables chemists to quickly and easily produce complex molecules. This reaction harnesses the controlled assembly of small molecules called monomers to generate polymers with specific properties. As the field of minisci grows, so will our ability to synthesise increasingly sophisticated molecules for various purposes.
All chemical reactions can be divided into: decomposition, combination, and rearrangement. This article will focus specifically on the rearrangement reaction, more commonly known as a minisci reaction. A minisci reaction occurs when two molecules collide and create a new molecule. The minisci three-component response is the most common type of minisci reaction. It takes place when three molecules collide and form two new molecules.
Mechanism of the Three-Component MiniSci Reaction
The Three-Component MiniSci Reaction is an organic reaction that allows for the synthesis of substituted benzamides. The reaction proceeds by forming an iminium ion, which is then attacked by a nucleophile. The mechanism of this reaction has been extensively studied and is a standard teaching tool in undergraduate organic chemistry courses.
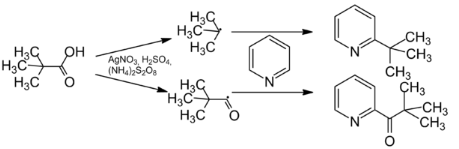
The Three-Component MiniSci Reaction is a valuable tool for synthesising substituted benzamides. The reaction is reliable and efficient and can be performed in various solvents.
The use of a base, such as triethylamine is critical to the success of the reaction. The dinitrobenzene intermediate can be isolated and purified if necessary. The use of a base, such as triethylamine is essential to the success of the response. The dinitrobenzene intermediate can be isolated and purified if critical.
Applications of the Three-Component MiniSci Reaction
A three-component miniSci reaction is a powerful tool for synthesising small molecules. It has a wide variety of applications, including preparing pharmaceuticals, agrochemicals, and other fine chemicals. The miniSci reaction is a simple and efficient process that can be performed under various conditions.
A three-component miniSci reaction is a valuable tool for synthesising small molecules. It is a simple and efficient process that can be performed under various conditions.
The reaction is a three-step process that is simple, efficient, and scalable. The first step of the response is activating the carboxylic acid with a hindered amine. This step is necessary to prevent the formation of an enamine intermediate. The second step is the addition of the amine to the activated carboxylic acid. This step forms the quinuclidine ring. The final phase of the reaction is the displacement of the chloride with alcohol.
- The three-component miniSci reaction can be used to synthesise a variety of different molecules
- It is a versatile reaction that can be used in a variety of applications
- Some of the potential applications of the three-component miniSci reaction include drug discovery, polymer synthesis, and the synthesis of natural products.
- The reaction is simple, efficient, and scalable and can be performed under mild conditions
- The reaction has been used to synthesise a variety of complex molecules, including natural products, pharmaceuticals, and agrochemicals
Drawbacks of Three-Component MiniSci Reaction Bulleted List
The three-component miniSci reaction is a popular synthetic method used in many laboratories. However, a few drawbacks to this reaction should be noted:
- The first drawback is that this reaction is often slow and can take a long time to complete.
- Secondly, the yield of the response is often low, meaning that not a lot of product is produced.
- Third, it requires three components which can be challenging to obtain in some developing countries.
- The miniSci reaction is not as efficient as the traditional two-component method.
- Lastly, this reaction is often not very selective, meaning that it produces many unwanted side products.
Conclusion
This article outlines a three-component minisci reaction that can be used to produce ketones. This reaction is a synthetic strategy employed in organic chemistry to build complex molecules in a single step. An electrophile, a nucleophile, and a leaving group comprise the three components. The reaction proceeds through a single intermediate, which is generated by colliding the nucleophile and the electrophile. The response is simple and can be performed in a variety of solvents.
 Profile
Profile Settings
Settings Refer your friends
Refer your friends Sign out
Sign out