Amines are organic chemistry molecules that feature a basic nitrogen atom and a lone pair as part of a functional group. Amines are generally ammonia derivatives generated by replacing one or more hydrogen atoms with an alkyl or aryl group. Alkylamines and arylamines are the most common types. In amines, two kinds of substituents are connected to a nitrogen atom, which is known as an alkyl. Amines are ammonia’s inorganic anion or spinoff. Vital amines encompass amino acids, biogenic amines, trimethylamine, and aniline. Diazonium salts are chemical compounds with a nitrogen–nitrogen triple bond.
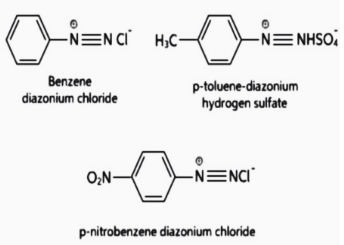
Diazonium Salt
A diazonium salt is a natural molecule with a nitrogen–nitrogen triple bond-like structure that can have an aryl or benzene ring and is an alkyl or alkane derivative. The ‘Salt’ portion of the name originates from the fact that diazo signifies ‘d-nitrogen’ in the compound. The chloride ion is a typical counter-ion to the positively charged nitrogen atom in this part’s ionic salt.
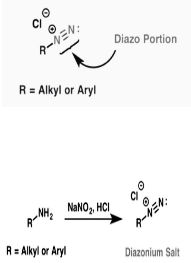
Making diazonium salts is a straightforward technique. In hydrochloric acid, alkyl or aryl primary amines are taken and reacted with sodium nitrite. Depending on the circumstances, this reaction occurs at or below room temperature.
Chemical Formula
Diazonium salts are organic compounds with the chemical formula R–N2+X–, wherein X might be halogens, hydrogen sulphate, or different organic compounds. Aryl diazonium salts are often used as chemical intermediates, where X may be an inorganic or organic anion, inclusive of a halogen, and R may be any organic institution, including alkyl or an aryl. The diazonium may be effortlessly replaced with the aid of several functional processes that can not be substituted without delay into the aromatic ring, together with –I, –OH, –F, –CN, and –H.
Diazonium Salt IUPAC Nomenclature
Arenediazonium salts include arene diazonium compounds. The word aza stands for nitrogen, and the phrase di stands for two in “diazonium salt.” The final two terms together suggest that the onium compound is ionic. As a result, diazonium salts are ionic compounds that contain N≡N.
Diazonium Salt Preparation
The diazonium salt is made by reacting benzene with nitrous acid to produce diazonium chloride at 273 to 278 degrees Celsius. Nitrous acid is generated inside the response mixture when sodium nitrite interacts with hydrochloric acid. The conversion of primary aromatic amines to diazonium ions is known as diazotization.
NaNO2 +HCl → HNO2 + NaCl
HNO2 + HNO2 → N+ = O + H2O + NO2–
Diazonium Salts Physical Properties
Here the physical properties of diazonium salts are described, which are as follows;
Many nitrate and perchlorate diazonium salts explode when diazonium salts are heated and left to dry. Separating the salts from it is nearly impossible. It is used to make synthetic preparations that are used in situ.
Diazonium and trifluoroborates are room-temperature stable double salts used to produce Naphthol-AS dyestuffs.
Diazonium salts are colourless crystalline substances that become black when exposed to oxygen.
Diazonium Salts Chemical Properties
Here the chemical properties of diazonium salts are described, which are as follows:
Reactions Involving Nitrogen Displacement
The diazonium group is formed when F, Cl, Br, I, CN, OH, and H are joined to an aromatic ring. Diazonium salts may be made from practically any primary aromatic amine, making them useful in synthesis. These react to form a wide range of chemicals. Diazonium salts are not the same as Grignard reagents. The amines needed to make diazonium compounds are quickly produced by combining them with nitrogen compounds.
Halogen as a replacement (Sandmeyer Reaction)
Cuprous chloride or cuprous bromide is combined with a freshly made diazonium salt solution to replace the Cl or Br diazonium group in this process. The asbestos is held at room temperature, or occasionally higher, where nitrogen is slowly created. After several hours, aryl chloride or aryl bromide can be extracted from the reaction mixture. The Sandmeyer reaction is called after this cuprous halide-based method.
ArN2+ X– → ArX + N2
CN has taken over (Synthesis of Carboxylic Acids)
When cuprous cyanide reacts with a diazonium salt, the diazonium group is replaced by CN. To offset the effect of sodium carbonate and prevent cyanide loss in the form of HCN, diazonium solution is combined with cuprous cyanide.
ArN2+ CN– → ArCN + N2
Conclusion
Diazonium salts are useful in chemical reactions as well as in everyday life. It is primarily used to produce aryl derivatives. Diazonium salts are also used to produce cyanobenzene. In diazonium salts, a diazo group is substituted. They are also used in the dye and pigment industries. It can also insert -F, -Br, -Cl, -I, -NO2, -OH, and -CN groups into the aromatic ring, which is used as an intermediate.
 Profile
Profile Settings
Settings Refer your friends
Refer your friends Sign out
Sign out