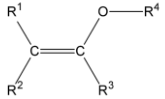
Alkenes containing alkoxy substituents are known as enol ethers. Since oxygen atoms provide double bonds in electrons by establishing a resonant configuration with the associated oxonium ion, the enol ethers and enamines act as active olefins or electron-rich olefins. Due to this feature, they may be used as substrates in organic processes such as the Diels-Alder process.
The ether of an equivalent enolate is referred to as enol ether. Methyl vinyl ether and 2,3-dihydrofuran are two simple enol ethers. In terms of chemical characteristics, enol ethers are placed between olefins and enamines. Wislicenus, the first to make ethyl vinyl ether, subsequently described its halogenation, hydrolysis and polymerisation.
Applications of Enol Ether
Polymerisation Reaction
The UV-induced photo-polymerisation of enol ether monomers occurs using diaryliodonium salt photoinitiators. The existence and steric mass of the substituents affect the polymerisation rates. Although photo-polymerisation of 2,3-dihydropyran gives higher polymers, oligomerisation and polymerisation of 4,5-dihydro-l,3-doxepin and 1-methoxy-1-cyclohexene, correspondingly, occurs. The variations in cyclic enol ether polymer disability are mostly related to the steric factors.
Hydrolysis Reaction
The hydrolysis of 1-cyclopropyl vinyl methyl ether exhibits sluggish proton transfer process features. Thus, the cis-and trans-2-aryl vinyl ethers need not interconvert throughout hydrolysis; hence, protonation of the carbon-carbon double bond is the rate-determining stage in such molecules.
Addition Reaction
The effects of adding chlorine and bromine to vinyl esterification results in an extremely fast reaction, as in the case of alkyl vinyl organic solvents, that requires refrigeration. At quite a range of roughly 0°C, the reaction can take place. Bromination occurs even without a catalyst, whereas chlorinations necessitate the use of peroxides to prevent polymerisation.
Reactions and usage
Enol ethers, like enamines, are electron-rich alkenes because the heteroatom donates electrons via pi-bonding. Oxonium ions characterise enol ethers. Enol ethers have a particular reactivity due to their bonding condition. They are more susceptible to attack by electrophiles like Bronsted acids than simple alkenes. They also go through inverse request Diels-Alder processes.
The presence of alpha and oxygen linkers in enol ethers has a significant impact on the overall process. While vinyl ethers can undergo polymerisation to produce polyvinyl ethers. They are also used as inhalation anaesthetics in specific cases. The hydroperoxide is formed by the acid-catalysed sequential addition of hydrogen peroxide to vinyl ethers:
C2H5OCH=CH2 + H2O2 → C2H5OCH(OOH)CH3
Preparation
Enol ethers are not formed via the alkylation of enolates, even though they will be the ether of respective enolates. Removal reactions are used to make certain enol ethers from saturating ethers.
Instead, iridium-catalysed transesterification of vinyl esters, particularly the readily available vinyl acetate, could be used to make vinyl ethers using alcohols:
ROH + CH2=CHOAc → ROCH=CH2 + HOAc.
The interaction of ethyne with alcohol in the context of a base produces vinyl ethers.
Natural Occurrence
The Claisen reorganisation of enol ether chorismate to prephenate, an intermediary in the biosynthesis of phenylalanine and tyrosine, is catalysed by the enzyme chorismate mutase.
Synthesis of Pyrazoles using Enol Ethers
Enol ethers constitute common reactive species in chemical chemistry. Electrophiles are their immediate reaction partners. A reversal of electron demand occurs when one or more powerful electron-withdrawing molecules are introduced at the other end of double bonding from the alkoxy group. Under the circumstances of nucleophilic vinylic replacement, such activating enol ethers interact remarkably with diverse nucleophiles like amines, thiols, ethyl alcohol, or C-anions. Circular or compound samples are produced when bi- or trifunctional nucleophiles are used. Thus, activated enol ethers are trifunctional electrophiles that may be used to introduce a three-carbon segment into the resultant molecule. Enol ethers combine with hydrazines to make pyrazoles, amidines to create pyrimidines, hydroxylamine to generate isoxazoles, and anilines to shape quinolines/ones.
Conclusion
In chemical science, an enol ether seems to be an alkene containing an alkoxy group. R2C=CR-OR is the underlying framework, wherein R is hydrogen, alkyl, or aryl. Vinyl ethers with the formula ROCH=CH2 are a subgroup of enol ethers. The chemical 3,4-dihydropyran, monomer methyl vinyl ether and ethyl vinyl ether are essential enol ethers. Since the oxygen atom provides electrons to the double bond by establishing a resonance configuration with the associated oxonium ion, enol ethers and enamines are known as active alkenes and electron-rich alkenes. Thus, they are reactive substrates in some organic processes, including the Diels-Alder process. The ether of equivalent enolate could be considered as an enol ether, thus the term. Ethyl vinyl ether and 2,3-dihydrofuran are two simple enol ethers.
 Profile
Profile Settings
Settings Refer your friends
Refer your friends Sign out
Sign out