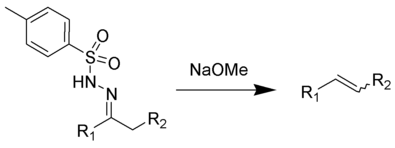
When the Tosyl hydrazone of an aldehyde or ketone is treated with Na in ethylene glycol, a Bamford–Stevens reaction occurs, which results in the synthesis of alkene. NaOMe, NaH, LiH, NaNH2, and other strong bases are also used. Side reactions are widespread, and the orientation of the double bond means that a thermodynamic product containing a high proportion of substituted alkenes is generated. In either protic or aprotic solvents, the process can be carried out. It is possible to synthesise alkenes from tosyl hydrazones using the Shapiro and Bamford-Stevens reactions.
Carbocation and carbenoid mechanisms are two of the options. While the carbenoid mechanism prefers aprotic solvents, the carbocation mechanism prefers protic solvents. They have an impact on the final product’s quality. Either of the two processes can separate the diazo molecule.
Bamford-Stevens Reaction
Unsaturated compounds can be synthesised from Tosylhydrazones via the Bamford-Stevens reaction. Di-azo derivatives are formed when the mono-anion reacts with a base and decomposes in the presence of heat.
Tosyll-hydrazone mono-anions are widely decomposes thermally to provide Diazoalkanes, which can be employed in various ways, such as the functionalization of solid supports and the epoxidation aldehydes, and the research of radicals and carbenes.
Bamford-Stevens reaction Sulfonylhydrazones can be treated either with sodium metal (Na) in the presence of a proton source is used, and only enough sodium metal is added to react with one of the two hydroxyl groups) or with sodium metal (Na) in an aprotic solvent such as methylbenzene [toluene, Ce] without a proton source.
Other Key Details
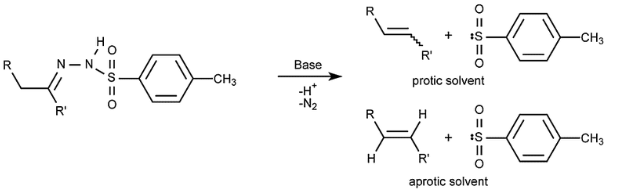
With the help of an acid catalyst, aldehydes and ketones undergo the Bamford-Stevens reaction, resulting in alkenes and cyclopropanes. Here, in organic synthesis, there are numerous essential general reviews. Aprotic and protic Bamford-Stevens procedures categorise the responses because they are typically performed in protic or aprotic solvents.
Other bases, e.g. NaOMe, alkali metal hydrides, and NaNH2, were also utilised in the reaction of Tosylhydrazones with sodium in ethylene glycol to yield alkenes (Bamford-Stevens reaction). In contrast to the Shapiro reaction, side reactions occur in these situations, and the more strongly substituted alkene is primarily generated. A carbenium ion mechanism and a carbene mechanism are proposed for these reactions, which take place in aprotic solvents. Diazo chemicals serve as intermediates in both scenarios, and they can be isolated in some cases.
Carbene compounds are often synthesised through the photolytic, thermal, or transition metal catalysed breakdown of Diazoalkanes. Bamford-Stevens reaction is a variation on the catalysed breakdown of Diazoalkanes, which yields carbenes and carbenium ions in aprotic solvents. Another option is to use chemicals to stimulate halogen removal from gem-dihalides or HX from a CHX molecule (or another strong base). The formation of free carbenes in these reactions is not certain. There is evidence that a metal-carbene complex forms when a free carbene is not present in some cases.
Mechanism Involved
During the first step of the Bamford-Stevens reaction, Tosylhydrazone is treated with a base, resulting in the diazo compound A.
Carbocation C in an aprotic solvent and a carbene B in an aprotic solvent make up the reaction process. Protic solvents produce E-alkenes primarily, whereas aprotic solvents produce mainly Z-alkenes. A higher proportion of the more substituted alkene is created when there is a choice of products.
While deprotonation of hindered Arene sulfonyl hydrazones is possible, the standard Shapiro conditions generally do not yield any alkene if a-Methine proton must be removed in the initial deprotonation step. Shapiro claimed that LDA was able to solve the problem. However, further research shows that this change is unsuccessful in other cases. When the conventional Shapiro and Bamford-Stevens conditions failed, lithium t-Butyl Amide was preferable in one example. At the same time, in another, an aprotic Bamford-Stevens reaction was required to react with the aforementioned N-Aminoaziridine derivative.
Mechanism of Carbocation
An alkene mixture is created when the diazonium ion formed by abstracting a proton from solvent loses N2 to give the equivalent carbocation. Diazo compounds are decomposed into carbenes and Z-alkenes via a 1, 2-hydrogen shift in an aprotic solvent.
Diazo compounds are synthesised using the Bamford-Stevens reaction. It is a variation of the Shapiro reaction. This reaction uses alkyl lithium and Grignard reagents, while the other reaction uses Na, NaOMe, and NaH as well as many additional bases. Consequently, the Shapiro reaction produces less-substituted olefins (kinetic products), whereas the Bamford-Stevens procedure creates more-substituted olefins (the thermodynamic products).
Conclusion
Bamford-Stevens decomposition of Tosylhydrazones has been applied to steroids, but not extensively. A diazo molecule that decomposes quickly is the catalyst for the reaction. A Wagner-Meerwein-type rearrangement is commonly present in the Wagner-Meerwein-type decomposition in proton-donating solvents. The diazo molecule appears to give carbene intermediates in aprotic solvents, which lead to olefins and insertion products after the reaction is completed.
 Profile
Profile Settings
Settings Refer your friends
Refer your friends Sign out
Sign out






