This article will mainly discuss the 5 postulates of the Kinetic theory of gases. We will also get an answer to the question, “What are the three main points of the Kinetic theory of gases?”. But first, we need to understand what is meant by the kinetic theory of gases.
James Clerk Maxwell, Rudolf Clausius, and Ludwig Boltzmann developed the Kinetic theory of gases. This theory tries to explain the macroscopic properties in terms of the motion of the molecules present in it.
What is the Kinetic theory of gases?
The Kinetic Theory of Gases states that the gaseous particles will be in a constant motion and undergo perfectly elastic collisions. And also, average kinetic energy will be proportional to absolute temperature.
![]() Following are the assumptions of the Kinetic theory of gases.
Following are the assumptions of the Kinetic theory of gases.
What are the three main points of the Kinetic theory of gases?
The following are the three main points of the Kinetic theory of gases.- When molecules collide, there is no loss or gain of energy
- The molecules in a gas take up little space in relation to the container they are in
- The molecules are always moving in a straight line
Assumptions of Kinetic theory of gases:
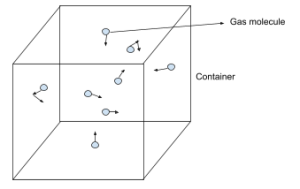 Following are the assumptions of the Kinetic theory of gases.
Following are the assumptions of the Kinetic theory of gases.
- Gas molecules are constantly moving in random directions
- Gas molecules travel in a straight line
- Gas molecules are tiny compared to the distance between them, and the volume of the molecules is negligible
- Average Kinetic energy is dependent on absolute temperature
- During the random motion of molecules, there will be elastic collisions
- The motion of gas molecules is based on Newton’s laws of motion
- The time interval of collision between any two molecules is minimal
5 Kinetic theory of gases:
This is also known as the postulates of the Kinetic theory of gases. Following are the 5 postulates of the Kinetic theory of gases.- Gas is made up of numerous molecules that move at random
- Intermolecular interactions are negligible
- Collisions between molecules and between molecules and container walls are always elastomeric
- The average kinetic energy of all molecules is temperature-dependent
- Gas molecules are tiny compared to the distance between them, and the volume of the molecules is negligible
Factors affecting the behaviour of gas molecules:
- Temperature(T)
- Volume(V)
- Pressure(P)
- Number of molecules(n)
Formulas based on Kinetic theory of gases:
There are few formulas which are obtained from Kinetic theory of gases and few of them are as follows.- Total Kinetic energy of the gas:
- RMS Speed:
- Boltzmann constant:
- Pressure of gas:
Applications:
All ideal gas laws are proven by the kinetic theory of gases. Following are the ideal gas laws.- Boyle’s law: Pressure(P) of the gas is inversely proportional to the volume(v) at constant temperature(T) i.e.P ∝ 1v
- Charle’s law: Volume(v) is directly proportional to the temperature(T) at constant pressure(P) i.e.v ∝ T
- Gay Lussac’s Law: Pressure(P) is directly proportional to the temperature(T) at constant volume(v) i.e.P ∝ T
 Profile
Profile Settings
Settings Refer your friends
Refer your friends Sign out
Sign out




