Force
A push or pull on an object that occurs as a result of the object’s interaction with another object is referred to as force. Any physical quantity can now be represented by its dimensions.
Force=mass×acceleration
The dimensional formula of force can be given:
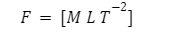
Effects of Force
- Changes in the position of the body
- To modify one’s body’s speed
- To shift one’s body’s direction
- To speed up a moving body
- To decelerate or bring to a halt
Types of Forces
Contact forces and non-contact forces are the two types of forces:
- Contact Forces: Contact forces include muscular forces, mechanical forces, and frictional forces that are in direct contact with the body where the force is to be delivered or are in contact through a medium.
- Non-contact Forces: Non-contact forces are defined as forces that function without the use of a medium or direct touch with the body. Examples of non-contact forces include magnetic forces, electrostatic forces, and gravitational forces.
SI Unit of Force
The International System of Units (SI) is a widely used measurement system. Newton is the SI Unit (N). Let’s look at how it was calculated.
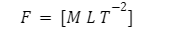
We know that,
SI Unit of mass = kg
SI Unit of length = m
SI Unit of time = sec
Thus, unit of force = kgm/s²
This is referred to as Newtonian mechanics. It is indicated by the letter N. In the metric system, this is also the unit of force. It is a regularly used measurement unit in science.
1N=kgm/s²
Other Units of Force
Besides Newton, there are additional units of force. However, they are not as widely used as the SI unit. Let’s have a look at what they have to offer.
Dyne (Dyn): In the CGS system, a dyne is a force unit. 1 dyne is the force required to move an object with a mass of 1g and a speed of 1 cm/s². When working with little items, this unit is usually utilised.
1 gcm/s²=1dyn
1 dyn=10-5N
Poundal (pdl): When a 1 pound item is subjected to a 1 foot/second2 acceleration, the force applied is 1 poundal. The FPS (foot-pound-second) system has this as a unit. It’s rarely used in scientific calculations.
Unit of Force = pound-foot/second²
1 lb.ft/s²=1 pdl
1 pdl=0.138254954376N
Gram Force (gf): This is a new force unit in the CGS system. The force applied on an object of mass 1 g owing to gravitational acceleration is defined as 1 gramme force. Pond (p) is another synonym for gram force.
1p=1gf
1gf=0.00980665N
Pound Force (lbf): Pound Force is another force unit in the FPS system. The force operating on an object of mass 1 avoirdupois pound owing to Earth’s gravity is defined as 1 pound-force. This is a non-technical phrase for force that is recognised as an object’s weight.
1 lbf =4.448222 N
Kip: One kip equals 1000 pounds of force. It is mostly utilised by civil engineers in situations where pound-force is insufficient for big loads.
1 kip=1000 lbf
Ton Force: The force exerted by Earth’s gravity on an object with a mass of one tonne is known as the 1 ton-force.
1 tf=9806.65 N
Ounce Force (ozf): The force imposed on an item of mass 1 ounce owing to the Earth’s gravitational acceleration is known as 1 ounce force.
1 ozf=116lbf
1 ozf=0.278014 N
Sthene: 1 sthene is defined as the force applied to a 1 tonne object to give it a 1 m/s2 acceleration. The MTS (metre-tonne-second) system has this unit.
1 sthene=1 ton.m/s²
1 sthene=1000 N
Kilogram Force (kgf): The force exerted by Earth’s gravitational field on an object of mass 1 kg is known as a kilogram-force.
1 kgf=9.80665 N
1 kgf=1000 gf
Conclusion
A force is an external agent that is applied to a body in order to modify the state, speed, direction, or location of the body. The amount and direction of force are both vector quantities. The force’s direction is known as the force’s direction, and the location where force is applied is known as the point where force is applied. It is measured with a spring balance, with the unit of force being Newton (N).
 Profile
Profile Settings
Settings Refer your friends
Refer your friends Sign out
Sign out




