Distance
Distance is defined as the numerical measurement of the distance between two objects. Distance refers to the physical length or estimation in everyday life when it comes to physics mechanisms. In many circumstances, the distance between A and B (for example, two nations over) is equivalent with the distance between B and A.
Distance is used as a function or metric in physics to simplify the understanding of physical distance. There is a general agreement on what it means for portions of a place to be “close to” or “far away” from one another.
Distance is a non-numerical measurement in psychology. Psychological distance refers to the various ways in which an object might move using time as a reference quality in a social distance, space, presumably, and self, along a dimension.
Distance Measurement
We can measure distance in various units, it can be cm, m or km. Cm or centimetre is a CGS system of units.
According to the International System of Units, the metre is the SI unit of distance. It’s a distance measuring unit that’s more like a conventional unit.
We may generate alternative units of various physical characteristics such as volume, area, acceleration, and speed using a metre as a base unit and some formulae.
Metric System
The development of the metric system of units, which was officially accepted in France in 1799 and is now used in most countries throughout the world, is one of Napoleon’s lasting legacies. The metre is the most basic metric unit of length, initially defined as one ten-millionth of the distance between the equator and the pole on Earth’s surface. Because French astronomers in the seventeenth and eighteenth centuries were pioneers in estimating Earth’s size, it was only natural to base the new system on their findings.
A definition defined in terms of the size of Earth has practical limitations, as someone desiring to know the distance between two points is unlikely to go out and re-measure the planet. As a result, a platinum-iridium metal bar was used to create an intermediate standard metre in Paris. This bar was defined at exactly one metre in length by international agreement in 1889, and precise copies of the original metre bar were made to serve as standards for other nations.
The metre is the foundation for all other length units. 1 kilometre (km) = 1000 metres, 1 centimetre (cm) = 1/100 metre, and so on. Even traditional British and American units like the inch and mile have been replaced by the metric system.
Metric Unit of Distance
The metric units of distance are formed from the CGS and MKS units of the system.
- CGS system = centimetre
- MKS system = metre
Other units of distance are:
- 10 metres = 1 decametres
- 10 decametres = 1 hectometres(hm)
- 10 decimeters = 100 metres
- 10 hectometres = 1 kilometres
- 10 hectometres = 1000 metres
Redefinitions of the Metre in the Modern Era
The formal definition of the metre was revised once again in 1960. The metre was redefined to equal 1,650,763.73 wavelengths of a particular atomic transition in the element krypton-86 as a result of improved technology for generating spectral lines of precisely known wavelengths. The benefit of this reclassification is that anyone with a properly equipped laboratory may replicate a standard metre without having to refer to a specific metal bar.
The metre was redefined once more in 1983, this time in terms of light velocity. In a vacuum, light may cover a distance of one metre in 1/299,792,458.6 seconds. As a result, light travel time is now our primary unit of measurement. In other words, a distance of one light-second (the amount of space covered by light in one second) equals 299,792,458.6 metres. In just one second, light travels almost 300 million metres; light travels really quickly! We might just as easily use the light-second as the fundamental unit of length, but for practical reasons, we’ve chosen to define the metre as a fraction of the light-second (and to follow tradition).
Large Distance Measurement
Metre scales are only useful for short distances. However, we can’t use a metre scale to measure great distances like planet to planet or star to star. To measure it, we’ll need a greater scale.
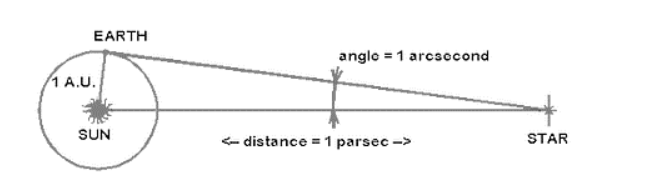
We employ units like the light year, parsec, and astronomical units to measure enormous distances. The average distance between the earth and the sun is measured in the Astronomical Unit. The average distance between the earth and the sun is approximately 1.496×1013 cm, or 93 million miles.
A light year is another unit for measuring distance. The distance travelled by light in a year is called a light year. 9.46×1017cm=1 light year .
The mean radius of the earth’s orbit, measured in parsecs or pcs, is one second of arc. In astronomy, it is the unit of distance. The parsec is a unit of measurement for distances between stars and galaxies.
1 parsec = 3.26 light years = 296,265 Astronomical Unit
Conclusion
To put it another way, distance refers to how far an object or person has moved. It’s a scalar quantity that measures an object’s total/complete path travelled. There can never be a negative or zero distance. It will always be in the affirmative.
The metre (m) is the SI unit of distance, while the centimetre (cm) is the C.G.S. unit of measurement for distance.
 Profile
Profile Settings
Settings Refer your friends
Refer your friends Sign out
Sign out




