Power in AC circuits is defined as the amount of energy delivered per unit of time by the circuit. It is used to calculate how much total power is required to run a load.
In an AC circuit, the power factor is defined as the ratio of real power (P) and apparent power (S).
The power factor can be expressed as a decimal or as a percentage.
Alternating Current
A current that varies its magnitude and polarity in regular intervals is known as an alternating current. It also can be described as an electrical current which changes or reverses direction on a regular basis.
Power
Electrical power is the rate at which energy is consumed inside a circuit. Therefore, all electrical and electronic devices and gadgets have a maximum amount of electrical power they can safely handle.
Types of Power
In a DC circuit, electrical power is described as the multiplication of voltage and current.
Mathematically:
IR = V
In AC circuits, however, the situation is more complicated. There are three categories of abilities here:
- Active power
- Reactive power
- Apparent Power
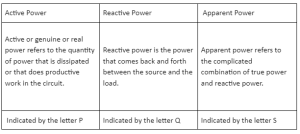
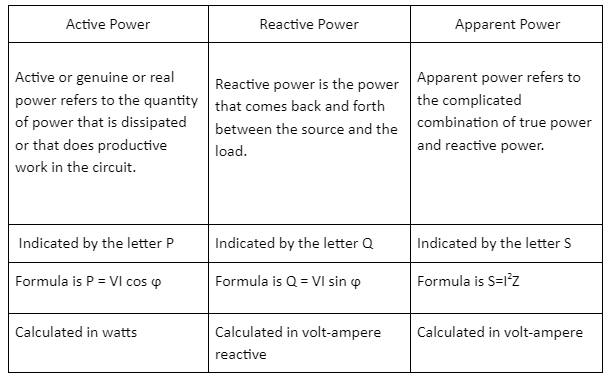
Active Power
Active or genuine or real power refers to the quantity of power that is dissipated or that does productive work in the circuit.
In power systems, it is calculated in watts but is more commonly expressed in (kilowatts) and (megawatts).
It is equivalent to an average amount of P=VI cos ϕ and is indicated by P (capital).
The circuit or load is driven by the desired output of an electrical system.
P = VI cos ϕ
Reactive Power
Reactive power is the power that comes back and forth between the source and the load. Reactive power, indicated by the letter Q, is the component that is proportionate to VI sinϕ
This is a power, but it is not calculated in watts because it is a non-active power, so it is calculated in Volt-Amperes-Reactive (VAR). The load power factor determines whether this reactive power is negative or positive.
This is due to the fact that inductive loads absorb reactive power, whereas capacitive loads create it.
Q=VI sin ϕ
Apparent Power
The term apparent power refers to the complicated combination of true power and reactive power. The perceived power is equal to the multiplication of voltage and current, regardless of phase angle.
The perceived power is helpful in determining the rating of power equipment. It can alternatively be written as the square of current times the impedance of the circuit.
It is indicated by the symbol S and is calculated in volt-amperes, with (kilovolt-amperes) and (megavolt-amperes) as practical units.
S=P+jQ
Or we can write as, S = I²Z
Power Triangle
A power triangle is the relationship between active power, reactive power and apparent power that can be explained by describing numbers like the vector in the geometrical form.
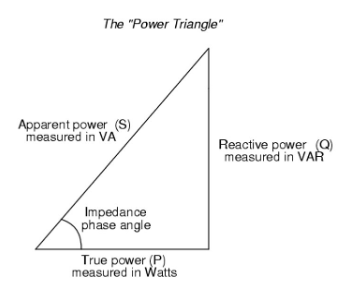
The total of the squares of two sides (active power and reactive power) equals the squares of the diagonal, according to the Pythagoras theorem (apparent power). i.e.,
S²=P²+Q²
That is, S = √((P²+Q²))
Power Factor
The ratio of the genuine power running across the circuit to an apparent power existing in the circuit is known as the power factor of the alternating current.
Power Factor = True power/Apparent power
Also, cosΦ = R/Z
Here, R represents resistance and Z represents impedance.
Importance of Power Factor
Power factor is critical because it dictates the quantity of currents flowing through the circuit and, as a result, the wire size that must be used.
This factor has an impact on the voltage and current waveforms.
A low Power factor indicates that a great deal of energy has been wasted as heat as a result of inefficient electricity use, which can lead to overheating and equipment failure.
Comparison between Active Power, Reactive Power and Apparent Power
Conclusion
Electrical power is the rate at which energy is consumed inside a circuit. All electrical and electronic devices and gadgets have a maximum amount of electrical power they can safely handle. In AC circuits, three categories of abilities are there:
- Active power,
- Reactive power
- Apparent Power
Active power is represented by the letter P and calculated in watts. Whereas reactive power is represented by the letter Q and calculated in volt-ampere reactive. Apparent power is represented by the letter S and calculated in volt-ampere.
A power triangle is the relationship between active power, reactive power and apparent power.
 Profile
Profile Settings
Settings Refer your friends
Refer your friends Sign out
Sign out