Toroid is a doughnut-shaped hollow circular ring with several turns of insulated wire twisted so close together that there is no room between them.
When high inductances are required at low frequencies, a toroid can be thought of as a circular solenoid utilized in an electric circuit as an inductor.
Michael Faraday, a physicist, invented the first toroid in 1830. He found that when the magnetic field changed, the voltage in a wire changed as well. Faraday’s law of induction is the name given to this phenomenon.
Magnetic effects of current
Electric current has three different impacts. They are the magnetic, thermal, and chemical effects. A magnetic field is formed around a wire when an electric current flows through it, and the deflection of a compass can be used to identify this. The magnetic field has a magnitude and a direction. If the electric current goes north to south, the magnetic compass will deflect clockwise, showing that the magnetic field’s direction is determined by the electric current’s flow direction. Magnetic lines are thought to emerge from the north pole and combine at the south pole, according to conventional wisdom. Two magnets’ magnetic field lines cannot cross each other. As the electric current via the wire grows, so does the magnitude of the magnetic field. Tesla is the SI unit for magnetic field.
Electricity and magnetism are inextricably linked, and it has been demonstrated that when an electric current runs through a copper wire, it generates a magnetic effect.
Toroid
A toroid is an electrical component made out of a hollow circular ring wound with a number of copper wire turns. To add permeability and enhance the generated inductance for a certain number of turns of copper wire, the ring is commonly formed of powdered iron or ferrites.
The material of the ring (permeability), the type of wire, and the number of turns the wire is twisted create a magnetic field or frequency; the total size also contributes. These pulses are employed as a counterweight in electronic systems like line filters to minimize noise.
Toroidal cores for transformers are becoming more popular than regular solenoid cores because magnetic flux leaks are reduced due to the toroidal shape versus the straight solenoid shape of the latter. The overall functionality is simply increased inductance with minimum electromagnetic interference to the circuits or equipment in the vicinity.
Calculation of magnetic field of a toroid
The Ampere circuit law is used to compute the magnetic field of a toroid.
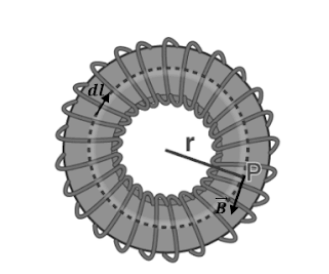
Consider a hollow circular ring that is coiled with numerous turns of current-carrying wire. Allow the magnetic field B to exist at point P, which is inside the toroid, in the diagram above. The loop is seen above as an amperian loop that forms a circle through point P, resulting in concentric circles within the toroid.
The magnitude at all places in the circle is equal due to the symmetric field, and the field is tangential.
Therefore, we can write:
∅B dl=B ∫dl=2πrB
The net current crossing the area is NI if the number of turns in the loop is N and the current flowing through the coil is I.
On applying ampere law:
∅B⋅dl=μ0NI
🡺2πrB=μ0NI
🡺B=μ0NI / 2πr
As a result, we can deduce that the magnetic field B is variable and not uniform over the cross-section.
Differences between solenoid and toroid
Electromagnetism is at the heart of both solenoid and toroid operation. One of the parallels between the two is this. However, there is a distinction between a solenoid and a toroid in that the amount of electric current in a toroidal coil is more than in a solenoidal coil of the same size.
- The solenoid has a cylindrical form but the toroid has a circular form.
- In a solenoid, the magnetic field is formed outside the solenoid, whereas in a toroid, the magnetic field is formed within the toroid.
- Inside the solenoid, the magnetic field is uniform. Inside the toroid, the magnetic field is not uniform.
- The magnetic field equation for a solenoid is given as: B=0NI whereas the magnetic field equation for a toroid is given as: B=0NI2πr.
Similarities between solenoid and toroid
- Both are based on the electromagnetic concept.
- When an electric current is supplied to both, they behave like electromagnetic materials.
- The magnetic field generated by the toroid and the solenoid are identical.
Conclusion
A toroid is a closed loop formed by joining the ends of a cylinder. Inductors and transformers are frequently made with toroidal coils. In these applications, the main advantage of toroidal coils over regular coils is magnetic field confinement; the magnetic field outside of a toroidal coil may be kept to a minimum. This decreases the risk of interactions between this field and other nearby fields and structures.
 Profile
Profile Settings
Settings Refer your friends
Refer your friends Sign out
Sign out




