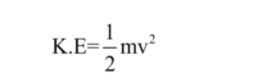If there is a need to move an object or we can say that if we have to put any object in motion, we will have to apply the force on the object so that it will accelerate. And to apply the force we will have to do some work, while doing the work some energy will get transferred, and that transferred energy will be termed as kinetic energy and kinetic energy will depend on the mass and the velocity of the object.
What is Kinetic Energy?
Kinetic energy is defined as the energy of motion. Kinetic energy exists in any object that moves, whether vertically or horizontally.
The kinetic energy of an item is the amount of work it performs as a result of its motion. It is a property of a moving object or particle that is affected by both its speed and its mass.
It should be noted that motion can be of any type, such as translation, rotation on an axis, vibration, or any combination of motions.
There are several types of kinetic energy by virtue of its motion: vibrational (energy resulting from vibrational motion), rotational (energy resulting from rotational motion), and translational (energy resulting from translational motion)
Note – We perform various acts daily that involve Kinetic energy, such as walking, jumping, swimming and throwing etc.
Let’s understand kinetic energy with an example, take the example of a moving car.
Cars in the motion have some kinetic energy. This is due to that they have mass and velocity. Considering the kinetic energy formula, we now know that when comparing a lorry and a sedan going at the same velocity on a road, the lorry will have more kinetic energy due to its larger size. Because kinetic energy is related to the mass of the moving object, a truck has more kinetic energy than a vehicle.
Formula for Kinetic Energy
Kinetic energy is directly proportional to mass and velocity of the object, and it’s formula is
Where, m = mass of the object v = velocity of the object
Temperature and Kinetic Energy
Let’s understand the concept of how kinetic energy is related to temperature.
Have you ever seen in the cold weather that people use a bonfire in their living room to get some heat. As soon as the fire starts burning the room gets warmer, but here what is happening is that the air inside the living room is getting warm.
Let’s understand it according to the kinetic theory of gases, all gases consist of various microscopic molecules and they move in a straight line until they collide with another gas molecule or any object. And the same thing is happening in the living room, energy from the fire gets transferred to air molecules and that transfer of energy causes the molecules to move faster and to collide with each other.
According to the formula of kinetic energy, we can see that it is directly proportional to the speed of molecules and that’s why whenever the speed of colliding molecules increases the average kinetic energy of total gas molecules also increases. And in this case if someone wants to measure the speed of any individual gas molecule it seems to be impossible.
But to measure kinetic energy, first calculate the average kinetic energy of all the molecules in the gas and for calculation of average kinetic energy the temperature of the room can be used.
Since when a collision occurs and gas molecules gain more and more energy and it starts moving faster than before the temperature also increases, which happens in the living room when someone burns fire.
Now, to calculate average kinetic energy of all the gas molecules the value of temperature of the gas should be known.
Formula for average kinetic energy
The formula for average kinetic energy of all the gas molecules is given by
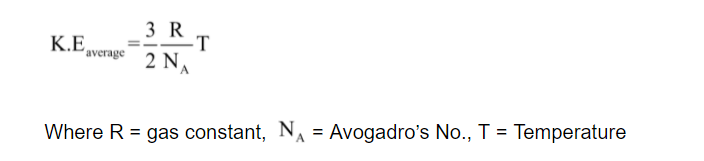
Temperature & Average Speed
We have to Calculate the root mean squared speed, or RMS speed, to gain an approximation of the average speed of the molecules in a gas. The square root of the average of each individual velocity squared is the RMS speed of the molecules. For example, if three objects moved at speeds of 9 m/s, 6 m/s, and 3 m/s, the group’s RMS speed would be 12.041 m/s.

There is a relationship between the RMS speed of gas molecules and the average kinetic energy in the gas because particles in motion have kinetic energy, and kinetic energy increases with speed. This signifies that the RMS speed and temperature have a relationship. The average kinetic energy (K) is calculated by multiplying one-half of each gas molecule’s mass (m) by the RMS speed squared.

Conclusion
The kinetic energy for gas molecules have totally different scenario than the kinetic energy of any object, there is only concept of translational kinetic energy when we talks about the gas molecules and when the temperature of the surrounding increases it directly affects the speed and collision of gas molecules that results in the increase of average kinetic energy. Hope this article will help you in understanding the relationship between the temperature and the kinetic energy.
 Profile
Profile Settings
Settings Refer your friends
Refer your friends Sign out
Sign out