Temperature-Definition
Temperature is defined as the measurement of how hot or cold a body or an object is. Temperature can be felt by coming in contact with the object or the body. We can say that the temperature is the degree of coldness or hotness of a body. If the object feels hot its temperature is high and if a body feels cold its temperature is low. The S.I. unit of temperature is Kelvin (K). The other general unit of temperature is the degree of Celsius. Temperature can also be measured in degrees Fahrenheit. Temperature is present in all matters. The measurement of temperature is usually done with an instrument called a thermometer. The temperature of an object or a body changes depending on the heat applied to the body or heat extracted from the body. When heat is applied to a body or object, the temperature of the object rises, and when heat is extracted from the object or kept in a cold atmosphere, the temperature decreases.Types of the Temperature scale
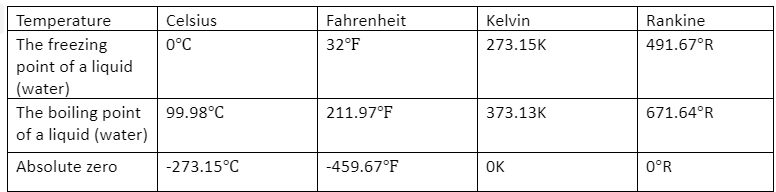
The major types of temperature scales that are used in our day to day life, in industries, and Science are Fahrenheit and Celsius Scale – these two types of temperature scales are generally used every day in our house for measurement of weather, body temperature, etc; the scales of temperate that is used in the industries and sciences are the absolute zero-based Kelvin scale and Rankine Scales.Fahrenheit Scale
The Fahrenheit scale was first developed in the early 18th century by a scientist of German named Daniel Gabriel Fahrenheit and its measurement standards were adopted from the scale introduced by Ole Roemer. In some parts of the Caribbean and the United States, Fahrenheit temperature scale is used commonly. In the case of water, it boils at 212 degrees Fahrenheit and the water freezes at 32 degrees Fahrenheit. This type of temperature scale also includes the temperature below 0℉. The lowest temperature on the Fahrenheit scale is -459.67℉.Celsius Scale
For measuring temperature, the Celcius scale is mostly used all over the world except in the United States, there were two versions of the Celsius scale which were invented in the first half of the 18th century, one version was created by Anders Celsius, who was a Swedish Scientist and the other version was created by French Jean Pierre Cristin. The Celsius scale is based on a 100 division or differences between the boiling point and the freezing point, so the Celcius scale is also known as the centigrade scale. On the Celcius, scale water boils at 100℃ and freezes at 0℃ degrees Celsius. This type of temperature scale also includes a temperature below 0. The lowest temperature on the Celcius scale is -273.15℃.Kelvin Scale
In the 19th century Kelvin temperature scale was taken from the Celcius scale by a British scientist named William Thompson and later was introduced by Lord Kelvin. The Kelvin scale was designed in such a way that the temperature scale’s zero point is located at the absolute which means the absolute zero for Kelvin Scale is located at 0 K. Kelvin scale is largely used in scientific calculations and equations. Kelvin is used as a standard unit in case of measuring the relationships between pressure, volume, mass, and temperature. There is no degree notation used in Kelvin.Rankine Scale
The Rankine scale of temperature was introduced and invented in the 19th century just after the introduction of the Kelvin scale by a Scottish scientist named William John Rankine. This type of temperature scale is not largely used except in some engineering fields of the U.S. At 0° Rankine, the absolute zero is located. The boiling point of water in the case of Rankine is 671.67°R and water freezes at 491.67°R.Different temperature scales are related in the following way
Celsius scale and Fahrenheit scale. The Celsius scale is divided into 100 parts and the Fahrenheit scale is divided into 180 parts, the freezing point of the Celsius scale is 0°C and the freezing point of the Fahrenheit scale is 32° F. So the relationship can be written as C-0/100 = F-32/180- C/100 = F-32/180
- C/10 = F-32/18
- C X 18/10 = F – 32
- 9/5*C = F – 32
- 9/5*C + 32 = F
Difference between Heat and Temperature
| Heat | Temperature |
| Heat is a type of energy produced. | Temperature is the degree of coldness or hotness of an object or body. |
| In a body or an object, the measurement of total kinetic energy is heating. | In a body or an object, the measurement of average kinetic energy is temperature. |
| Heat cannot be directly measured by any instrument | The thermometer is an instrument that is used for measuring temperature. |
| Heat is the cause. | Temperature is the effect. |
| Heat is a derived quantity | Temperature is a fundamental quantity. |
| SI Unit of heat is Joule (J) | SI Unit of temperature is Kelvin(K) |
 Profile
Profile Settings
Settings Refer your friends
Refer your friends Sign out
Sign out