Variable forces are intriguing to learn about because most of the forces we face on a daily basis are variable in nature. When a force is applied in the direction of the force, it is said to do work on a system if the system moves in that direction. Integration is required in the event of a variable force to calculate the amount of work done. A constant force of magnitude F, as we know, that moves an object by a distance of x can be expressed as L: W = F. Δx. Here work done is expressed as W and the displacement that the force causes is expressed as x. We now will discuss the concept with the Force-Displacement Plot graph.
How work is calculated when the force is variable using the work done by a variable force formula:
Integration is used to determine the amount of work done by a variable force. Force exerted on an object attached to an open-ended horizontal spring, for example, can be expressed as:
Fs = -kx
Here:
- The spring constant is k in this example.
- Attached objects are displaced by x
We can see that this force is proportional to the object’s displacement from equilibrium. Therefore the force acting at each instant throughout the compression and extension of the spring will be different.
As a result, the total amount of effort is calculated by adding up the minuscule amounts of work done at each instant.
Thus, the integral can be evaluated as:
Ws=Fxdx= XiXfkdx
The Force-Displacement Plot:
Force (in N) and displacement (in m) are the two axes on a force-displacement graph. The graph’s area is equal to Fs. The amount of time spent working on the object is represented by this number.
- We can read forces and displacements directly from a force-displacement plot.
- We can calculate the force’s output by tracing the graph’s x-axis.
- The increase in kinetic or potential energy is what the item experiences as a result of the force being applied here.
Example:
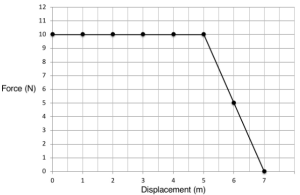
The following graph displays the force used to move an object over a distance of 10 meters. Please respond to the following question:
- When was the object subjected to a constant force?
- In this case, how much force was used when the object moved 6m away.
- How much work was done on the item?
-
![]()
Solution:
- Between 0 and 5 m in displacement, a constant force of 10N was applied.
- To figure out how much work has been done on the object, we need to find the area under the graph. The sum of the areas in each rectangle and triangle on the graph is calculated in this manner.
Displacement as a result of variable force:
- Displacement is essential for any kind of activity. No matter how much energy the force transfers to the object, it achieves nothing if the displacement is zero.
- Potential or thermal energy are examples of the forms of energy that the transferred energy is absorbed in, rather than effort.
- This equation clearly demonstrates how much work is done when a force is applied and a displacement is caused.
Gravity:
You can either raise the force or use a greater distance to improve your output if you’re going for it. Gravity forces us to work against it in our daily lives.
Lifting objects against gravity, or even just walking, falls under this category.
As a result of the gravitational force, we are forced to work harder than otherwise.
How kinetic energy plays its role:
- When an object is subjected to a force in a system where there are no unbalanced forces, the displacement can theoretically approach infinity. For instance, the amount of effort done is inconceivably large. This, however, is incorrect.
- The kinetic energy of the item on which the work is done is a more precise work description. These findings are known as the work-energy theorem, and they are one of the most significant in science.
Work-energy rule:
- Work-energy theorem says that an instantaneous force’s work on an item equals the object’s kinetic energy gain. Ten newtons of force applied to an object at rest results in the kinetic energy of the item being ten times greater than what it was before the force was applied.
- Accordingly, we can conclude that an item in indefinite, constant motion is still able to perform finite work. As a result, the object’s kinetic energy remains constant due to its perpetual motion. Defining “positive” and “negative” work can be done with the help of the work-energy theorem. An item must undergo a positive change in kinetic energy to perform positive work.
- As a result, the applied force should increase the object’s kinetic energy. A force that results in a decrease in kinetic energy is said to be doing negative work. A force’s overall work output could be positive even if it was initially negative.
- This implies that the object’s kinetic energy should be increased due to the applied force. A force that results in a decrease in kinetic energy is said to be doing negative work. A force’s overall work output can be positive, even if it was initially negative.
- As long as you don’t change the object’s velocity, you don’t make any effort. Instead, a shift in potential energy indicates an energy shift.
Conclusion:
Thus we conclude the subject of work that variable force does. There are a lot of non-conservative factors that we encounter in our daily lives, which means that their work depends on the direction they take. As a general rule, non-conservative forces can be quite erratic. These are the factors that change throughout time or location. As the object moves, its kinetic energy changes, and so does the amount of work done by these forces. Take into account how much work was done at each point along the route. The sum of all the infinitesimal values approaches 0 as the component values get smaller and smaller.
 Profile
Profile Settings
Settings Refer your friends
Refer your friends Sign out
Sign out