Introduction
We generally describe the movement of bodies in how they move. Assuming an item moves to such an extent that it rehashes its way routinely later equivalent timespans, its movement is supposed to be occasional. Such movement is portrayed by the rakish recurrence, where the body dislodges by some point at some speed called the precise speed given by, Here, Ω = 2 πf, Ω is the rakish speed, and f is the recurrence. This movement can be addressed by a sinusoidal wave as displayed below:(the image will be transferred soon)You have found in schools that each talk is apportioned a proper timespan. This proper timespan is known as the time span . The educator coming and leaving your class every day is the intermittent movement of your instructor.
Body
Periodic Motion
On the off chance that a body repeats its movement along a clear way, about a specific point later a decent time frame is known as the occasional movement. The proper timespan later in which the movement is rehashed is known as the time of movement. The prerequisite that the movement of a body or an article should fulfil to be occasional is that it has an authoritative period where minimal timespan later which the intermittent movement of a body rehashes the same thing is known as the period, T.
Two Examples of Periodic Motion
The movement of the hands of a clock. The movement of an hour’s hand is 12 hrs, of brief’s hand is 1 hour and the second’s hand of a clock is 1 minute. A straightforward pendulum, when pulled from its rest position aside and delivered, makes back and forth movement (oscillatory movement) is supposed to be occasional.
Non – Periodic Motion
The sort of movement in which the article rehashes its movement however not in a decent stretch or timeframe. We should take the case of a taxi administration that gives the between city administrations to the general population, however there are a lot of taxicabs to drop the travellers. Each taxi isn’t having a proper time frame and is not even certain which taxi would come to pick the travellers at a stop. Such a condition where the example isn’t fixed, the movement of these cabs is supposed to be in non-occasional movement.
Non-periodic movement models
The running of the batsman between the wickets.The swinging of the parts of the tree.
What is Periodic Function?
A body is supposed to be in intermittent movement on the off chance that the movement it’s executing is rehashed later equivalent time frames, similar to an armchair, a swing moving. An intermittent capacity can be characterised as:
A capacity getting back to similar worth at normal spans.
However intermittent movement and oscillatory movement sound something very similar, not all occasional movements will be oscillatory movement. The significant distinction between an occasional movement and oscillatory movement is that intermittent movement is pertinent to any movement that rehashes after some time. However, the oscillatory movement is remarkable to those movements that execute about a balance point or between two states. An occasional capacity can characterise every intermittent movement.
To comprehend the idea of intermittent capacity how about we consider a pendulum sway, wavering alongside its balanced position, the direction of the weave is displayed beneath, presently assuming the bounce is swaying then, at that point, its uprooting will likewise shift from zero to positive and back to nothing and negative, this can be effectively shown with a chart,
Periodic Function Formula
A capacity f is supposed to be occasional if, for some non-zero constant P, it is the situation that,
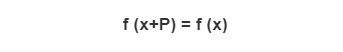
For all upsides of x in the area. A non-no steady P for which this is the case known as a time of the capacity.
Periodic Function Equation
We should take an instance of a swaying object, its removal in intermittent movement is addressed by a capacity which is occasional on schedule;
f(t) = Acosωt
We need to focus on the components of this capacity, the cosine work rehashes the same thing on schedule from geometry we know the accompanying;
cosθ = cos(θ+2π)
⇒ cos(ωt) = cos(ωt+2π) ——(1)
Suppose time period is T;
f(t) = f(t+T)
⇒ Acosωt= Acosω(t+T)
⇒ Acosωt = Acos(ωt + ωT) ——(2)
From equation (1) & (2) we can say that;
ωT = 2π
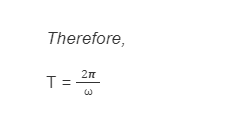
Subsequently, the time-frame of occasional movement is given by the above articulation,
The recurrence of this occasional capacity can be given when period, the recurrence is the number of motions per unit time, so assuming we know the ideal opportunity for one swaying then we can track down the recurrence by:

The development of planets around the sun, the movement of a yo-yo are for the most part instances of intermittent capacities. However, the case of a pendulum is a unique instance of intermittent capacity since it is executing basic symphonious movement. The distinction lies in how the movement is communicated numerically. Assuming the intermittent capacity can be addressed by a sine bend, then, at that point, the movement is supposed to be basic symphonious movement, similar to a load on spring swaying, a swing and so on Straightforward consonant movement is a kind of occasional movement where the reestablishing power is straightforwardly corresponding to the removal and acts toward the path inverse to that of relocation.
Recollect that the movement of a straightforward pendulum approximates to that of basic symphonious movement provided that the point is little.
Conclusion
Intermittent movement is the point at which the movement of an article consistently rehashes the same thing, for example, more than once moving this way or moving in a roundabout circle. In the event that a molecule in intermittent movement moves to and fro (To and Fro) over a similar way, then, at that point, this sort of movement is called Vibratory or Oscillatory Motion. Occasional time is the time period slips by from the second when a planet or comet leaves any point in its circle until it gets back to it once more.
 Profile
Profile Settings
Settings Refer your friends
Refer your friends Sign out
Sign out




