Definition of periodic motion
A body is said to exhibit a periodic motion when its motion on a definite path is repeated continuously within a specific time interval. The time interval after which the body’s motion is recurrent is called the time period. The universe is full of movements that continuously repeat themselves in patterns. The earth completes one rotation in 24 hours and one revolution in 1 year. In this case, the 24 hours taken to complete one rotation is the time period of the earth’s rotation, and 1 year is the time period of the earth’s revolution.
A body executes non-periodic motion when it does not repeat its motion after a definite time interval. For example, the motion of a bouncing ball is non-periodic.
Characteristics
To describe the periodic motion of any object, the following terminologies need to be understood first:
1.Time period: The time interval in which the body’s motion is repeated is called time period. It is denoted by T, and its SI unit is seconds. The graphs given below show time periods in different periodic motions.
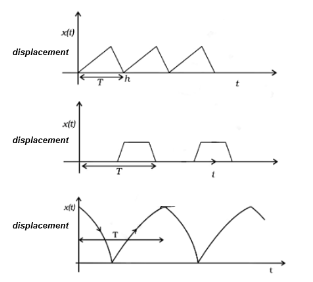
2.Frequency: It is the number of complete repetitions occurring per second (time period). Frequency and time period are inversely related to each other. As the SI unit of time is the second, the SI unit of frequency is cycles/second, which is the same as the unit Hertz (Hz).
Mathematically, frequency, denoted by v or f, is the reciprocal of the time period and can be written as:
f=1 ⁄ T
T=1 ⁄ f
3.Displacement: In a periodic motion, displacement is a function of time and, in general, can be represented as:
x(t)=Acosωt
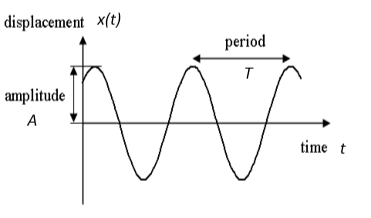
A denotes the maximum displacement from the particle’s mean position and is the angular frequency. If the angle ωt is increased by an integral multiple of 2π, the function becomes periodic. However, its value remains the same. The time period is then given by:
T=2π ⁄ ω
Hence, the displacement function is periodic with time period T.
x(t)=x(t+T)
Example of periodic motion
In nature, there are many examples of periodic motions, such as:
- In a year, the earth completes one revolution around the sun. The earth’s motion is periodic, and its time period is 1 year.
- Halley’s Comet orbits around the sun and is sighted on earth every 76 years. This is also an example of periodic motion over a time period of 76 years.
- The moon completes one revolution around the earth in 27.3 days. The moon’s motion is periodic, and its time period is 27.3 days.
- The motions of the hands of a clock are also periodic. The time period of a minute hand is 1 hour and that of the hour hand is 12 hours.
- Depending on the frequency of the tuning fork, it tines an equal number of times back and forth. For example, a tuning fork having a frequency of 256 Hertz has a time period of 0.00391 seconds.
Types
- Circular motion: A body moving in a circular path exhibits circular motion, which is periodic in nature as the motion is repeated after completing 360 degrees. For example, a particular compartment in a giant wheel moving in circular motion passes its initial point at regular time intervals, thus exhibiting periodic motion.
- Oscillatory motion: If the body exhibiting periodic motion moves to and fro with respect to a fixed equilibrium position along the same path, then the body possesses oscillatory motion. Every oscillatory motion is periodic in nature as it repeats itself after a fixed time interval. However, it is not necessary that every periodic motion is oscillatory in nature. For example, the motion of a moon is periodic but not oscillatory.
- Simple harmonic motion: An oscillatory motion for which the displacement is a sinusoidal function of time is simple harmonic motion. Kinematically, the to and fro motion of a particle about its equilibrium position, while moving in a linear path, is called ‘simple harmonic motion,’ given the force acting on it varies directly with its displacement and is in the direction of the mean position.
Simple pendulum
The arrangement of a simple pendulum consists of a heavy point-mass, known as the bob, suspended by a perfectly flexible, inextensible and weightless string attached to a rigid support. A simple pendulum oscillates back and forth with periodic motion when set to motion. It acts as a harmonic oscillator with a period dependent on the length (l) of its string and acceleration due to gravity (g). The periodic time is given by:

Conclusion
A body is said to exhibit periodic motion when its motion on a definite path is repeated continuously within a specific time interval. The time interval in which the motion of the body is repeated is called the time period. For a periodic motion, frequency is the number of complete repetitions occurring per time period. Frequency and time period are mathematically reciprocals of each other. For a motion periodic in nature, displacement is a function of time and is periodic with the time period.
In nature, there are many examples of periodic motions, such as the earth’s revolutionary motion, rotational motion, the sighting of Halley’s Comet, the motion of the hands of a clock and the tines of a tuning fork. All circular motions, oscillatory motions and simple harmonic motions are periodic. However, not all periodic motions need to be circular or oscillatory in nature.
 Profile
Profile Settings
Settings Refer your friends
Refer your friends Sign out
Sign out




