Introduction
What is a p-n junction?
A p–n junction is a boundary or interface between two types of semiconductor materials, p-type and n-type, within a single crystal of semiconductor. In the outer shells of the electrically neutral atoms on the “p” (positive) side there are more holes than electrons on the “p” (+ve) side, while there are more electrons on the “n” (negative) side. This allows only one direction of electrical current to travel through the junction. Doping, such as ion implantation, diffusion of dopants, or epitaxy, creates the p-n junction (growing a layer of crystal doped with one type of dopant on top of a layer of crystal doped with another type of dopant )..
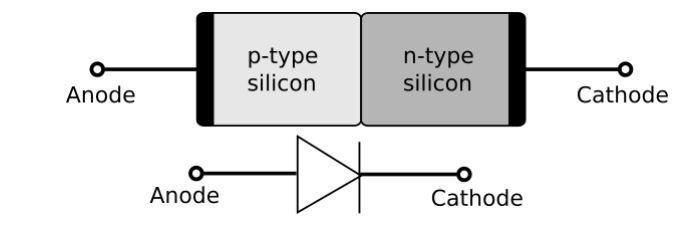
Properties
For modern electronics, the p–n junction has critical features. The conductivity of a p-doped semiconductor is comparatively high. The same is true of an n-doped semiconductor, but depending on the relative voltages of the two semiconductor zones, the junction between them can become depleted of charge carriers and hence non conductive. P–n junctions are often used as diodes, circuit devices that allow electricity to flow in one direction but not the other (opposite) direction, by managing this non-conductive layer. Bias is the application of a voltage across a p–n junction, with forward bias allowing for easy current flow and reverse bias allowing for little or no current flow.
Biasing
Equilibrium (zero bias)
Without an external applied voltage, a p–n junction reaches an equilibrium situation in which a potential difference arises across the junction. Built-in potential(Vbi) is the term for this potential difference.
The free electrons in the n-type are attracted to the positive holes in the p-type at the junction. They disperse into the p-type, where they join with the holes to cancel each other out. The positive holes in the p-type are attracted to the free electrons in the n-type in a similar way. The holes diffuse into the n-type, where they mix with the free electrons and cancel out. In the n-type, the positively charged donor dopant atoms are fixed in the crystal and cannot migrate. As a result, a region near the junction becomes positively charged in the n-type. The p-negatively type’s charged acceptor dopant atoms are fixed in the crystal and cannot migrate. As a result, a region near the junction in the p-type becomes negatively charged. As a result of the electric field created by these charged regions, a region near the junction acts to repel mobile charges away from the junction. The space charge zone, also known as the depletion layer, is formed when regions near the p–n interface lose their neutrality and most of their mobile carriers.
Forward bias of the p-n junction
When the p-type is linked to the positive terminal and the n-type to the negative terminal of the battery, the p-n junction is said to be forward-biased. The built in electric field at the p-n junction and the applied electric field are in opposite directions when the p-n junction is forward biased. When both electric fields are combined together, the resultant electric field is smaller than the built-in electric field. As a result, the depletion region becomes thinner and less resistive. When the applied voltage is high, the resistance of the depletion area becomes insignificant. At 0.6 V, the resistance of the depletion zone in silicon becomes entirely negligible, allowing current to flow freely over it.
Reverse bias of the p-n junction
The p-n junction is said to be reverse biased when the p-type is linked to the negative terminal and the n-type is attached to the positive side of the battery. In this circumstance, the applied electric field and the built-in electric field are both pointing in the same direction. The resultant electric field is in the same direction as the built-in electric field, resulting in a more resistive, thicker depletion area. The depletion region gets more resistance and thicker when the applied voltage is increased.
p-n junction formula
The p-n junction formula, which is based on the built-in potential difference induced by the electric field, is as follows:

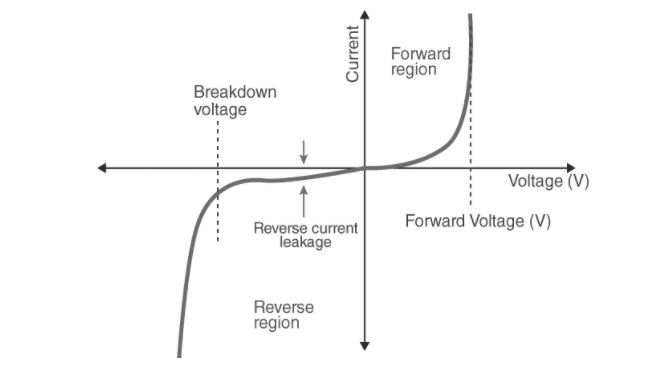
A curve between the voltage and current through the circuit defines the VI properties of PN junction diodes. The VI characteristics curve of the PN junction diode is shown in the graph above. In this curve, we can see that the diode works in three different zones, which are:
- Zero bias
- Forward bias
- Reverse bias
There is no external voltage delivered to the PN junction diode when it is at zero bias, which implies the potential barrier at the junction prevents current passage.
Applications of p-n junction diode
- When the p-n junction diode’s arrangement is reverse-biased, the diode can be used as a photodiode because it is sensitive to light.
- It has the potential to be used as a solar cell.
- The diode can be employed in LED lighting applications when it is forward-biased.
- Many electric circuits use it as a rectifier.
Conclusion
- The p-n junction is the fundamental component of all s/c devices. Understanding junction theory is essential for comprehending other s/c devices.
- Uncompensated -ve ions (N,’) on the p-side and uncompensated +ve ions (Np*) on the n-side create a p-n junction. As a result, a depletion region formed near the intersection.
- Drift current (due to the electric field) is balanced by diffusion current (due to concentration gradients of the mobile carriers) at thermal equilibrium.
- When +V is supplied to the p-side, a substantial current flows across the junction, however when —-V is applied, no current flows at all.
 Profile
Profile Settings
Settings Refer your friends
Refer your friends Sign out
Sign out




