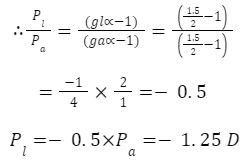Optics is a popular part of physics that deals with determining how light behaves and what properties it has. It also takes into account the interactions with the substance as well as the tools required to detect it. As a result, optics describes the behaviour of visible light, infrared light and ultraviolet light. Imaging is made possible by a system known as an image forming optical system, according to science.
Actually, optics is the study of how light affects the behaviour and visibility of materials. For exceedingly delicate surgery, we use light in the form of lasers. Also, thanks to the usage of fibre optic lines, we can watch a football match on TV. We can bend light using eyeglasses, microscopes, telescopes and mirrors, among other things.
Q1. A converging lens is used to form an image on a screen. When an opaque screen covers the upper portion of the lens.
(a) Half of the image will vanish.
(b) A skewed image will be created.
(c) The image’s intensity will drop, but the image will be complete.
(d) The image’s intensity will grow, but the image will remain blurry.
Answer: (c) The image’s intensity will drop, but the image will be complete. Because The focal length of the lens remains unchanged, the amount of light travelling through it is cut in half.
Q2. In optical fibres, the refractive index of the core is
(a) greater than that of the cladding.
(b) equal to that of the cladding.
(c) smaller than that of the cladding.
(d) independent of that of cladding.
Answer:(a) greater than that of the cladding.
Because for entire internal reflection to occur, The core’s R.I. must be greater than that of the cladding.
Q3. An object is placed in front of a plane mirror at a distance of 0.5 m. The distance between object and image will be equal to
(a) 0.25 m
(b) 0.5 m
(c) 1.0 m
(d) 2.0 m
Answer: (c) 1.0 m , because distance between the object and the image will be = 0.5 + 0.5 = 1.0 m
Q4. Air bubble in water behaves as
(a) sometimes concave, sometimes convex lens
(b) concave lens
(c) convex lens
(d) always refracting surface
Answer: (b) concave lens.
In water, an air bubble acts as a concave lens.
Q5. We combine two lenses, one is convex and other is concave having focal lengths f1 and f2 and their combined focal length is F. When the lenses are combined, they act like a concave lens, if
(a) f1 > f2
(b) f1 = f2
(c) f1 < f2
(d) f1 ≤ f2
Answer: (a) f1 > f2
Q6. The focal length of a biconvex lens of radii of each surface 50 cm and refractive index 1.5, is
(a) 40.4 cm
(b) 75 cm
(c) 50 cm
(d) 80 cm
Answer: (c) 50 cm as,
1/f = (μ-1) (1/R1 – 1/R2)
= (1.5-1) (1/50 + 1/50)
f = 50cm.
Q7. A metal coin is at the bottom of a beaker filled with a liquid of refractive index = 4/3 to height of 6 cm. A coin will seem at what depth to an observer gazing from above the liquid’s surface?
(a) 1.5 cm
(b) 6.75 cm
(c) 4.5 cm
(d) 7.5 cm
Answer: (c) 4.5 cm as
Apparent Depth=Real Depth/μ
= 6/(4/3) = 4.5cm.
Q8. Tom’ lenses of focal lengths ± 15 cm and ± 150 cm are available for making a telescope. What will be the focal length of the eyepiece to produce the largest magnification?
(a) + 15 cm
(b) + 150 cm
(c) – 150 cm
(d) – 15 cm
Answer:(a) + 15 cm.
For telescope magnification,
m = fo/fe
fe < fo
to achieve a high magnification.
Q9. If a convex lens of focal length 80 cm and a concave lens of focal length 50 cm are combined together, what will be their resulting power?
(a) + 6.5 D
(b) – 6.5 D
(c) + 7.5 D
(d) – 0.75 D
Answer: (d) – 0.75 D.
Focal length of the combination
1/F = 1/F1 + 1/F2 = 1/80 + 1/(-50)
P = 1/F = -0.75 D.
Q10. A convex lens and a concave lens, each having the same focal length of 25 cm, are put in contact to form a combination of lenses. The combination’s power (in dioptres) is
(a) zero
(b) 25
(c) 50
(d) infinity
Answer: (a) zero because
P = 1/F = 1/F1 + 1/F2 = 1/25 – 1/25 =0.
Q11. The refractive index of the material of an equilateral prism is √3. What is the angle of minimum deviation?
(a) 45°
(b) 60°
(c) 37°
(d) 30°
Answer:
(b) 60° Because at minimum deviation position,
r = A/2 = 30°
u = sini/sin r
sin i = μ×sin r = √3/2
i = 60°
Also, i+i =A + δ
⇒ 60 + 60 = 60 + δ
⇒δ=60°.
Q12. In the formation of a rainbow, the light from the sun on water droplets undergoes
(a) dispersion only.
(b) only TIR.
(c) dispersion and TIR.
(d) scattering.
Answer: (b) only TIR. Rainbows are generated when sunlight is dispersed by raindrops and entire internal reflection occurs within the raindrop.
Q13. A convex lens of refractive index 1.5 has a power of 2.5 D in air. If it is placed in a liquid of refractive index 2 then what will be the power of the lens?
(a) – 1.25 D
(b) – 1.5 D
(c) 1.25 D
(d) 1.5 D
Answer: (a) – 1.25 D as
P ∝ (μ-1)
(a) µ 1 = µ2
(b) µ 1 > µ2
(c) µ 1 < µ2
(d) µ 1 = 1/µ2
Answer: (a) µ 1 = µ2 as because
1/f = (μ-1) (1/R1 – 1/R2) and μ = 1
∵F=∞.
Q15. When a ray of light enters from one medium to another, then which of the following does not change?
(a) Frequency
(b) Wavelength
(c) Speed
(d) Amplitude
Answer: (a) Frequency Because When a ray of light travels from one medium to another, only its frequency changes.
Q16. A diver at a depth of 12 metres (pi = 4/3) observes the sky through a semi-vertical angle equal to
-
sin-14/3
-
tan-14/3
-
sin-13/4
-
90°
Answer: (c) sin-13/4
as the required angle can be given by
sin-11/μ = sin-13/4.
Q17. The objective and eyepiece make up an astronomical telescope. The focal length of the objective can be
(a) equal to that of the eyepiece.
(b) shorter than that of eyepiece.
(c) greater than that of eyepiece.
(d) The length of the eyepiece is five times shorter.
Answer: (c) greater than that of eyepiece. Because The objective’s focal length is higher than the eyepiece for achieving high magnification.
Q18. A 10 cm rod is positioned along the major axis of a concave mirror with a focal length of 10 cm, with its end closest to the pole 20 cm from the mirror. The length of the image is
(a) 10 cm
(b) 15 cm
(c) 2.5 cm
(d) 5 cm
Answer: (d) 5 cm.
 Profile
Profile Settings
Settings Refer your friends
Refer your friends Sign out
Sign out