Introduction
When an object changes its position in accordance with its surroundings with time, it is called motion. Motion is basically a change in the position of an object over a period of time. Motion in a straight line is a linear motion.
The main aspects of motion in a straight line is mentioned during this course which includes the difference in average velocity and speed.
Types of Linear Motion/Motion in straight line
The linear motion has two types which are as follows
- Uniform Linear Motion
- Non-Uniform Linear Motion
A body is in uniform motion if it travels the same distance in the same time interval. Uniform motion has no acceleration and constant velocity.
Whereas, a body is in non-uniform motion when it covers an unequal distance in an equal interval of time period. Non uniform motion has non zero Acceleration and the velocity is also variable.
Equation of motion in straight line
Calculus is the most suitable way to derive the equation of motion in a
straight line. When the value of the velocity-time, distance-time,
and Acceleration-time is known then the value of the others will be determined easily by differentiation or integration.
d(distance)/dt = velocity (v)
And
d(velocity)/dt = acceleration (a)
Formulas of motion in straight line
v=u+at
s=ut+1/2 at2
v2= u2+2as
Here,
v = final velocity
s = distance
u = initial velocity
a = acceleration
t = time
Speed
The distance travelled by a body in a unit interval of time is termed as speed. Speed is a scalar quantity which means that the speed has only magnitude. Speed does not have direction.
The speed is given by
Speed = Distance/Time
SI unit = meter per second = m/s
Average Speed
Average Speed is defined as the total distance travelled by a body in a given interval of time.
Average speed = total distance/ total time
Types of speed
There are two types of speed which we will learn.
- Uniform speed: A body is in uniform speed when it covers equal distance in an equal interval of time.
- Non uniform speed: A body is in non-uniform speed when it covers an unequal distance in an equal interval of time period.
Velocity
Velocity is a Physical Vector Quantity. Velocity has both magnitude and direction also. In calculus, velocity is defined as the first derivative of the position with respect to time period. Velocity is also defined as the rate of change in the position of an object w.r.t time.
SI unit = meter per second = m/s
Velocity = Displacement / Time
Velocity = (Final position – Initial position)/Time
Types of velocity
Constant Velocity: Velocity which does not change with the change in direction and speed and continues to move along the straight line is called constant velocity.
Changing Velocity: Velocity which changes with the change in direction and speed or changes with change in any of the two, direction or speed is called changing velocity.
Difference between Speed and Velocity
The difference between speed and velocity is very important as the questions related to this are always asked in the examination. Some basic differences of speed and velocity are given below.
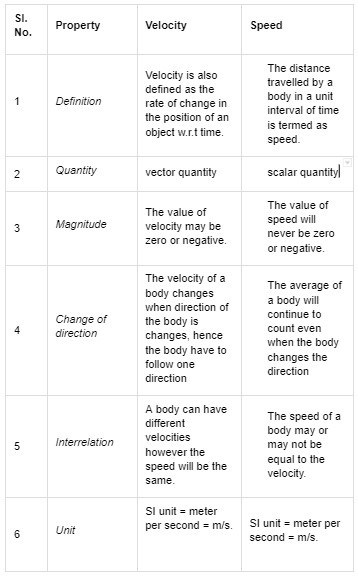
Conclusion
In maths, motion is defined in displacement, distance, velocity, acceleration, speed, and time. By connecting to the reference system, the movement of a body is observed. Also, the movement is measured based on the change in the body’s position relative to the frame.
In this article, we learn about motion in a straight line, speed, velocity and also speed and velocity difference.
The distance travelled by a body in a unit interval of time is termed as speed. SI unit = meter per second = m/s.
Velocity is also defined as the rate of change in the position of an object w.r.t time. SI unit = meter per second = m/s.
 Profile
Profile Settings
Settings Refer your friends
Refer your friends Sign out
Sign out




