A system of units is a collective list of units used to measure any item. Units are essential to understanding the measured value of a quantity. These units are used to relate and observe the measurement of any item, thereby understanding the magnitude of the quantity better. Length, mass and second are primary quantities that perform independently and combine to create more complex units. These fundamental quantities have different units in different systems. There are three systems of units, namely the C.G.S. system, F.P.S. system and M.K.S. system. Let’s briefly learn about each system in this article.
What are fundamental units?
In the system of units, physical quantities are measured based on their units. The fundamental quantities are the basic quantities that form the pillar of other derived quantities. The units that we use to measure these fundamental quantities are fundamental units. These fundamental quantities are the base for any measurement; other complex quantities are multiples of the units of these quantities. There were three different systems of the unit earlier developed to measure quantities but to avoid confusion. The global meetup reduced the three systems to a universal system, the International System of Units (S.I. units).
There are seven fundamental units in the S.I. unit system, where the length, mass, and time are the main quantities common in all three systems.
The list of fundamental units includes
- Length
- Mass
- Time
- Electric current
- Thermodynamics temperature
- Amount of substance
- Luminous intensity.
What is the C.G.S. system?
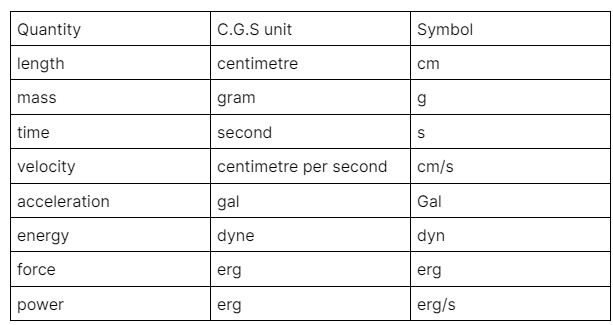
The C.G.S. system is a metric system of measurement. The full form of C.G.S. is centimetre-gram-second, and it’s widely used in the study of physics, especially in the fields of electrical and mechanical specialities. The system is based on using a centimetre as the unit of length, the gram as the unit of mass and the second as the unit of time, which is very similar to the S.I. unit system, a universally accepted system, but slightly varies.
In mechanical science, the units involve length, force, mass, pressure, energy etc. The flexibility of unit conversion is very direct. This flexibility is possible because the metric system behaves with the capacity to multiply or divide in powers of ten. The exponentials of tens are used to convert one unit system to another. For example, the unit of force in the S.I. The unit is Newton, and the unit of force in the C.G.S. system is dyne. The basic understanding of the metric system states 1m = 100cm and 1kg = 1000g; with these values we can convert Newton, which is expressed as 1 kg⋅m/s2, to dynes ( expressed as 1 g⋅cm/s2 ). Thus 1 newton will be equal to 100000 dynes.
Similar subtle conversions of S.I. units and C.G.S. systems are possible in electromagnetism and electrostatics. This system also has further subtypes like gaussian, electrostatic units (E.S.U.), electromagnetic units (EMU), and Lorentz-Heaviside units. The Gaussian units are the most widely adopted system of units in physics.
What is the F.P.S. system?
The F.P.S. system is a variant of the non-metric system, widely used in the states of the U.S. before the global audience universally accepted the S.I. unit. Still, some areas use this system to measure quantities like mass, length and time. The full form of the F.P.S. is a foot-pound-second system of units; this system uses the foot as the unit of length, the pound as the unit of mass and the second as the unit of time. The complex unit of speed and derived unit of force is the foot per second and poundal, respectively, where 1 poundal equals 1-foot pound per second squared.
What is the M.K.S. system?
The M.K.S. system of units also falls under the metric system and is very similar to the S.I. unit. The SI succeeded the M.K.S. system and followed the same units with more fundamental quantities. The full form M.K.S. is a metre-kilogram-second system of units, where the unit of length is metre, unit of mass is kilogram and unit of time is second. This system also has other derived units with length, mass, and time as the base units.

Conclusion
Progress would be impossible in science and technology if measurement and units weren’t there. May we achieve things with an individual system but present to a global audience a universal system. The three systems of units, namely, the C.G.S. system, F.P.S. system and M.K.S. system, were decided in different eras and constitute different parts of the world. The flexibility of the metric system allows these systems to co-exist in physics, though the main priority is given to S.I. units which is a close variant of the M.K.S. system.
 Profile
Profile Settings
Settings Refer your friends
Refer your friends Sign out
Sign out




