Linear motion is motion in one dimension. It is the most basic form of motion. It is when motion is along one line. Different paths describe different linear motions. Uniform linear motion is when the velocity is constant, or acceleration is zero. Non-uniform linear motion is when the velocity is not constant, or acceleration does not equal zero. The main difference between linear motion and non-uniform linear motion is that one is a scalar quantity and one is a vector quantity. In non-uniform linear motion, it is vital that we take direction also as a factor.
Does Uniform Linear Motion Exist?
It is very unlikely that uniform linear motion exists in day-to-day life. One example of linear motion is Newton’s first law of motion. The law states that when an object is in motion with no external forces acting on it with constant velocity, the object will continue to stay in motion.
However, in real life, motion on earth has many forces, like friction and gravity, making it a non-uniform motion. If we were to roll a ball in space that has no friction or gravity, then Newton’s law of motion is accurate, giving us uniform linear motion.
Displacement
It is the distance covered by the object in motion or the distance between the object’s initial placement and final placement. Displacement is linear and is measured in the units of length.
The formula of displacement is:
y = x’- x
Where,
- Initial placement = x
- Final placement = x’
- Displacement = y
Note that this is the displacement formula for objects in linear motion or one dimension only.
Distance is different from displacement. For example, a cab driver covers many destinations from the initial distance where he leaves his home. At the end of the day, he returns to the same place he initially started. Thus, the displacement is zero, but the distance is not zero.
Velocity
Velocity is the speed at which an object moves or is displaced. It is the rate of change of displacement over the rate of change in time.
The formula to calculate the speed of any object is:
d = s/t
Where,
- Distance = d
- Speed = s
- Time = t
Speed is still the magnitude, i.e., ms-1. Speed is scalar, whereas velocity is a vector quantity, considering directions.
Average Velocity
The average velocity is calculated using the total velocity and total displacement of the object in motion. The formula for average velocity is:
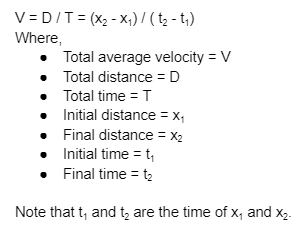
Instantaneous Velocity
In average velocity, we consider the whole motion from start to end of the object’s displacement.
But suppose there is a car on a highway. It is unlikely that the car stayed or had the same velocity throughout the journey. It must have encountered speed bumps, breaks, or tolls. Therefore, we can also consider its velocity in a given time period, i.e., in an instance.
Instantaneous velocity can be mathematically calculated using this formula:
V = lim(Δt→0) Δx / Δt = dx/dt
Acceleration
Acceleration is said to change in speed or velocity with time. It is also a second derivative of displacement. The SI unit is m/s².
To determine the average acceleration (A), we need to take the average velocity and divide it by time. Thus, the formula is:
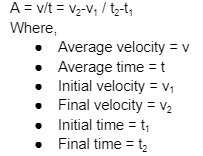
The instantaneous average may be calculated using the given formula:
A = lim(Δt→0) Δv / Δt = dv / dt = d² x / dt²
The 4 Equations of Kinematics
These equations are very essential to solve even basic problems in motion and kinematics They are:
s = ut + ½at² …. (1)
v² = u² + 2as …. (2)
v = u + at …. (3)
s = (u + v)t/2 …. (4)
Where,
- Distance = s
- Final velocity = v
- Initial velocity = u
- Time = t
- Acceleration = a
These equations give us a path to find the unknown values of some components using other components of motion. These equations are to be memorised for one to solve linear motion questions.
Solved Example
Q. A stone is thrown vertically upwards at a speed of 15m/s. How high will it go, and how much distance has been covered?
Here,
- u = 15m/s
A = 9.8 m/s² (gravity)
- Once it reaches its maximum height, v = 0.
Using kinematics equation 3, we get
0 = 15 – 9.8t
t = 15/9.8
t = 1.53 seconds
Distance = speed/ time
= 15/ 1.53
= 9.8 metres approx.
Conclusion
Linear motion is motion along a straight line. Different paths describe different linear motions.
Linear motion is always depicted using vectors and graphs, represented by the x and time component graph. If we were to plot a uniform linear motion graph, the plot would show a straight line across the graph as there is no change in direction or speed.
 Profile
Profile Settings
Settings Refer your friends
Refer your friends Sign out
Sign out




