If a charged particle moves through an electric field, it experiences an electric force. This force can be one of attraction or repulsion, depending on the particle’s charge.
The magnitude of the electric force on a moving charge in an electric field is equal to the product of the electric field and the charge of the particle. This force depends on the type of charge (positive or negative) and the amount of the charge on the particle.
Force on a moving charge in an electric field
The electric force is the force of attraction or repulsion between the two electrically charged bodies. The force is also known as the Coulomb force or Coulomb interaction. The strength of an electric field is defined as the electric force per unit charge.

Force on a Moving Charge in a Magnetic Field
A magnetic field is a field or a region around a magnet where the magnet’s influence can be felt on moving electric charges, currents or other magnetic materials.
When a charged particle moves in a magnetic field, it experiences a magnetic force. The magnitude of this magnetic force is directly proportional to the magnitude of the charge, the component of the velocity of the particle which is acting normal to the direction of the magnetic field and the magnitude of the applied magnetic field.
FqvB
F=kqvB
Here, q is the magnitude of the charge, vsin is the component of the velocity which is acting perpendicular to the direction of the magnetic field, B is the magnitude of the applied magnetic field, and k is the proportionality constant, whose value is equal to the 1 (k=1). Thus,
F=qvBsin
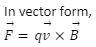
This is the required expression for the force acting on a moving charge in a uniform magnetic field, where the cross product tells that the velocity and the magnetic field are perpendicular to each other.
Force on a Moving Charge in Magnetic and Electric Fields
Lorentz force is the force that is exerted on the charged particles moving in a magnetic field and an electric field. The modern formula of Lorentz force was derived by the Dutch physicist Hendrik Lorentz in 1895.
Suppose a positively charged particle is moving in an electric and magnetic field. The sum of the magnitude of the electric force and magnetic force equals the total force acting on the particle. This total force is called the Lorentz force. It can be given by the following expression:
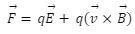
In this formula, the first term indicates the electric field while the second indicates the magnetic field. It can also be expressed by the following formula.
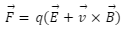
This equation gives the magnitude of the force acting on a moving charge in a magnetic and an electric field. This force is applied in Cyclotrons and other particle generators. The concept of this force is also seen in Cathode Ray Tube television to deviate the charged electrons in a linear path to land them on particular spots on the screen.
Difference Between Force on a Moving Charge in a Magnetic Field and an Electric field
S. No. | Magnetic Force | Electric Force |
1 | The magnetic force acts only when the charged particles are in the moving position in a magnetic field as it depends on the velocity of the particles. | The electric force acts on a charged particle in both rest or motion in an electric field as it does not depend on the velocity. |
2 | The force on a moving charge in a magnetic field is low compared to the electric field. | The force on a moving charge in an electric field is high compared to the magnetic field. |
3 | This force never acts centrally. | Electric force may or may not be central. |
4 | Electric force does not work on the charged particles in a magnetic field as it functions normal to the direction of motion. | Electric force works on the charged particles in an electric field. |
5 | The magnitude of the magnetic force is measured with the following formula. F=qvB | The magnitude of the electric force is measured with the following formula. F=qE |
Conclusion
Electric fields are generated from electric charges and varying magnetic fields, while the magnetic fields generated from permanent magnets and the electric charge which is in motion.
Force on a moving charge in magnetic and electric fields is the sum of the magnetic force and an electric force that acts on the charge in the respective fields, known as Lorentz force.
 Profile
Profile Settings
Settings Refer your friends
Refer your friends Sign out
Sign out




