As the name suggests, the particle accelerator is an acceleration machine that can be used to provide very high speed and energies to the charged particles to save them in well-defined beams. These accelerators are mainly used for research in the field of particle physics. A cyclotron is also a type of cyclotron that provides electric and magnetic fields in vacuum chambers to boost the speed of charge particles. In this article, we are going to study about a cyclotron.
![]()
![]() In any particle accelerator, the charged particle can be accelerated by applying an electric field. The force applied by the electric field on the moving particle can be given by the Lorentz force law:
F = qE + qV B
Where
F = force
E = electric field
q = charge
V = speed
B = magnetic field
Talking about the magnetic field, it works in the perpendicular direction of the motion, and it works in bending the trajectory of the particle into a spiral. The magnetic field applied in the cylinder presents in the same gap, so that the same bunch of particles can be accelerated many times. As the particle makes its way outward in a spiral route, the increase in speed is exactly balanced by the increase in distance between gap transits. That becomes the reason behind the bunch reaching the gap at the same point on the RF cycle every time.
The frequency of the orbit of a charged particle can be called cyclotron frequency, and it always remains in the perpendicular direction of the magnetic field. If the charge on the particle, mass of the particle, and strength of the magnetic field is known, we can calculate the force applied on the charge using the following formula.
f = qB/2m
By the above formula, we can easily understand that whenever a charged particle passes by a gap, the electric field applies a force on it. Using this phenomenon, we can calculate the frequency in the following way:
f = v/2R
With the cyclotron frequency equation to yield:
v = qBR/m
The kinetic energy can be given by the following:
E = mv2/2 = q2B2R2/2m
R is the radius where the energy is to be determined.
In any particle accelerator, the charged particle can be accelerated by applying an electric field. The force applied by the electric field on the moving particle can be given by the Lorentz force law:
F = qE + qV B
Where
F = force
E = electric field
q = charge
V = speed
B = magnetic field
Talking about the magnetic field, it works in the perpendicular direction of the motion, and it works in bending the trajectory of the particle into a spiral. The magnetic field applied in the cylinder presents in the same gap, so that the same bunch of particles can be accelerated many times. As the particle makes its way outward in a spiral route, the increase in speed is exactly balanced by the increase in distance between gap transits. That becomes the reason behind the bunch reaching the gap at the same point on the RF cycle every time.
The frequency of the orbit of a charged particle can be called cyclotron frequency, and it always remains in the perpendicular direction of the magnetic field. If the charge on the particle, mass of the particle, and strength of the magnetic field is known, we can calculate the force applied on the charge using the following formula.
f = qB/2m
By the above formula, we can easily understand that whenever a charged particle passes by a gap, the electric field applies a force on it. Using this phenomenon, we can calculate the frequency in the following way:
f = v/2R
With the cyclotron frequency equation to yield:
v = qBR/m
The kinetic energy can be given by the following:
E = mv2/2 = q2B2R2/2m
R is the radius where the energy is to be determined.
What is a cyclotron?
A cyclotron can be considered a type of particle accelerator. This type of particle accelerator was invented and patented by Ernest O. Lawrence in 1929–1932 at the University of California, Berkeley. This type of particle accelerator is used to accelerate a charged particle. Using the acceleration from a cylindrical vacuum chamber, the particle moves in a spiral path from the centre of the chamber. To maintain the spiral path of the particle, the chamber provides a magnetic field, and the acceleration of the particle is maintained by the electric field provided by the same chamber in a rapidly varying manner. Being the first cyclic accelerator is the reason for the naming of this particle accelerator as a cyclotron. One of the main differences between this accelerator and other accelerators like the Cockcroft-Walton accelerator is that the other accelerators are capable of providing electric fields only once.How to construct a cyclotron
Cyclotrons are not so simple to construct because a simple cyclotron requires very expensive components like highly magnetised magnets, vacuum system, RF transmitting gear, etc. The basic structure of any cyclotron can be made by placing two hollow metallic chambers at a small distance along the diameter. These chambers can be called ‘Dee’ because of their shape. After placing them in such a situation, we are required to make a vacuum around the dees, and it needs to be connected to an oscillator. After the connection is made, a perpendicularly flowing strong magnetic field is required. The below image represents the structure of a cyclotron: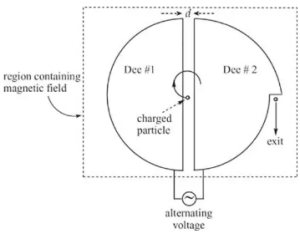
Working of a cyclotron
The below image represents the working of a cyclotron: In any particle accelerator, the charged particle can be accelerated by applying an electric field. The force applied by the electric field on the moving particle can be given by the Lorentz force law:
F = qE + qV B
Where
F = force
E = electric field
q = charge
V = speed
B = magnetic field
Talking about the magnetic field, it works in the perpendicular direction of the motion, and it works in bending the trajectory of the particle into a spiral. The magnetic field applied in the cylinder presents in the same gap, so that the same bunch of particles can be accelerated many times. As the particle makes its way outward in a spiral route, the increase in speed is exactly balanced by the increase in distance between gap transits. That becomes the reason behind the bunch reaching the gap at the same point on the RF cycle every time.
The frequency of the orbit of a charged particle can be called cyclotron frequency, and it always remains in the perpendicular direction of the magnetic field. If the charge on the particle, mass of the particle, and strength of the magnetic field is known, we can calculate the force applied on the charge using the following formula.
f = qB/2m
By the above formula, we can easily understand that whenever a charged particle passes by a gap, the electric field applies a force on it. Using this phenomenon, we can calculate the frequency in the following way:
f = v/2R
With the cyclotron frequency equation to yield:
v = qBR/m
The kinetic energy can be given by the following:
E = mv2/2 = q2B2R2/2m
R is the radius where the energy is to be determined.
In any particle accelerator, the charged particle can be accelerated by applying an electric field. The force applied by the electric field on the moving particle can be given by the Lorentz force law:
F = qE + qV B
Where
F = force
E = electric field
q = charge
V = speed
B = magnetic field
Talking about the magnetic field, it works in the perpendicular direction of the motion, and it works in bending the trajectory of the particle into a spiral. The magnetic field applied in the cylinder presents in the same gap, so that the same bunch of particles can be accelerated many times. As the particle makes its way outward in a spiral route, the increase in speed is exactly balanced by the increase in distance between gap transits. That becomes the reason behind the bunch reaching the gap at the same point on the RF cycle every time.
The frequency of the orbit of a charged particle can be called cyclotron frequency, and it always remains in the perpendicular direction of the magnetic field. If the charge on the particle, mass of the particle, and strength of the magnetic field is known, we can calculate the force applied on the charge using the following formula.
f = qB/2m
By the above formula, we can easily understand that whenever a charged particle passes by a gap, the electric field applies a force on it. Using this phenomenon, we can calculate the frequency in the following way:
f = v/2R
With the cyclotron frequency equation to yield:
v = qBR/m
The kinetic energy can be given by the following:
E = mv2/2 = q2B2R2/2m
R is the radius where the energy is to be determined.
 Profile
Profile Settings
Settings Refer your friends
Refer your friends Sign out
Sign out




