The argument related to the concept of attraction of things towards one another and towards different surfaces has been going on since the 4th century BC. Sir Isaac Newton proposed the logical concept to put clarity to this concept. Along with this clarification, he also proposed many other laws, like the laws of inertia, mass, acceleration, and motion. Moreover, Newton did state the universal law of gravitation as related to Kepler’s. The article provides a detailed derivation of Newton’s law of gravitation.
Newton’s Law of Universal Gravitation
Sir Isaac Newton brought out his works on universal gravitational force theory along with his set of mathematical and philosophical works in the year 1687. The law of universal gravitation was not a mere theory because Newton supported it with mathematical calculations.
According to Newton’s law of universal gravitation, every object or matter in this universe attracts others by some force. This force is called gravity. The mathematical formula of gravity can calculate the force.
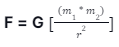
where,
F → force of gravity
G → gravitational constant
m1 → mass of the first object
m2 → mass of the second object
r → distance present between the centre of the objects
The gravitational force between two different objects with mass and size is inversely proportional to the square of the distance between their centres and directly proportional to the product of the two masses.
Discovery Of Gravitational Force
The story of an apple falling from a tree has more to it. Newton did not observe just the apple falling for proposing the law. Even in the apple fall, Newton observed that the apple was attracted to the ground when the acceleration of the apple increased, which was initially zero when the apple hung still. He realised that it would still fall to the ground even when the apple was at the tallest point. There he suspected some force in action.
He then assumed that this force would be why the Moon revolves around our planet. It could be illustrated and inferred from an experiment of shooting a cannon from the top of a hill. Newton proposed that when a cannon was shot at a velocity, the cannonball would never reach the surface; instead, it would keep rotating around the Earth.
Derivation Of Newton’s Law of Gravitation
According to Newton’s law of universal gravitation
F ∝ m1 × m2

Where the value of the gravitational constant is 6.67 × 10-11 N m2 kg-2
Kepler’s Laws
Kepler’s laws are quite similar in theories to Newton’s gravitational law. Kepler’s laws deal with the movement of the planets in space.
- First law – The first law says that the planets are in motion around the Sun in an elliptical orbit, where the Sun is fixed at one point of focus. It is the reason for the cycles of the seasons.
- Second law – The radius vector from the focus of the Sun to the point of the planet occupies an equal amount of areas in an equal amount of time intervals. This statement proves the law of momentum conservation.
rmin + rmax = 2a × (major axis length)
- Third law – The values of the square of the revolution time of a planet in an elliptical orbit and the cube of the planet’s semi-major axis are directly proportional to each other.
T2 ∝ a3
The time taken to revolve around the Sun is longer when the orbit of the particular planet is longer.
Applications Of Gravitational Force
The real-time scenario of applying the law and calculation of gravitational field is employed in the following aspects.
- Newton’s law of gravitation is useful in calculating the value of the masses of the stars like the sun, the planets, and their satellites like the moon.
- It aids in identifying and locating new celestial bodies like planets, stars, satellites, comets, etc.
- It is used to determine or forecast the celestial bodies’ trajectories in motion.
- It helps calculate the numerical value and the range of the pull of objects towards each other in the universe or even space.
- A planet’s gravity decides how far it will hold its atmosphere within it.
- The gravitational forces exerted by the stars decide the capacity of the star to hold its gases around itself. It applies to the black holes, too, where gravity is assumed to be enormously high.
Conclusion
Newton’s law of universal gravitation explains why things are attracted to the Earth’s surface. The theory was made a law when proper mathematical calculations and derivations were given. The search for finding the attraction of things towards the surface started in the 4th century BC. Aristotle was the first one to start it. Many scientists proposed their theories but failed to succeed in proving them. Finally, Newton’s law of gravity was accepted worldwide. The law has devised a formula to calculate the force of gravitation between two objects. Newton did state the universal law of gravitation and proved it wisely.
 Profile
Profile Settings
Settings Refer your friends
Refer your friends Sign out
Sign out




