Geopotential is the pressure exerted by a given water weight because of gravity and atmospheric pressure acting upon it. Geopotential can be calculated for any point on the Earth’s surface, given the potential sea level and its height above sea level (elevation) are in metres or feet.
The difference between an object’s potential energy at a given altitude and the potential energy of an identical object at sea level is equal to the amount of energy needed to shift the said object from the sea altitude to the given height.
About geopotential
Geopotential at the surface of the Earth has a magnitude equal to zero. This surface is called the geopotential surface and is also referred to as a geoid in modern times. Geopotential can also be described as gravitational potential per mass. The symbol of geopotential is Φ.
Geopotential unit
We define ‘work’ as force * distance. It has units of Joules (J). Hence, the work required to lift a mass at a certain height is J kg-¹.
Considering a Joule is also defined as a Newton multiplied by metre, where
Newton = kg m s -²
We can substitute the aforementioned value for J to yield an alternative geopotential unit: m² s-²
Formula of geopotential
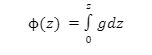
Here,
z – height above the surface
g- gravity at each height
Geopotential is measured using geoid models derived from satellite altimeter measurements rather than surface meteorological data. Due to its simplicity, it is used extensively as a part of a geodetic network for measuring elevations, heights and weights for gravity calculations and computing Earth tides.
What is geoid?
The geoid is the surface of an imaginary sphere whose radius equals the Earth’s mean radius. It is defined by elevation above or below the mean sea level at a particular point. It can be thought of as the ‘ideal’ sea-level surface. There are no mountains, hills, valleys or other topographical features that would distort the measurement.
The geoid has been calculated using data from satellite altimeters carried by satellites such as GASP, GRACE and SeaWinds. This provides a reference surface that can calculate geopotential heights in the entire world.
What is geopotential height?
It is a common misconception that geopotential height is the same as the global mean sea level. Geopotential height or geopotential surface altitude is the height above sea level of an imaginary planetoid surface (geoid). Based on the geopotential surface, we can calculate global heights when the ocean and atmospheric pressure are known when calculating the geopotential at any point.
Geopotential height is used for many purposes in geophysics, such as calculating Earth tides, gravity field analysis and finding the relative position of two points on Earth. In geodesy, geopotential height can be used to calculate the heights and weights of two points on the Earth’s surface relative to each other.
Geopotential height formula
A geopotential height is calculated by dividing the geopotential at height (z) by the gravitational acceleration on the Earth’s surface (go). It is denoted by the capital ‘Z’. The geopotential height formula is as follows:

Here,
go is a constant = 9.8 ms-²
z = geometric height
Importance of geopotential
Geopotential is essential in physical volcanology. It is commonly used along with heat flow and gravimetric data to determine the state of stress and structural conditions at depth.
Geopotential is also helpful in determining whether or not a volcano will erupt, along with other parameters such as heat flow, gravity anomalies and surface deformation.
In soil mechanics, geopotential can be used to determine the degree of saturation for a given area based on the topographic relief of the land surface. This is done using a method known as geopotential evapotranspiration, which can be used over large areas (e.g., entire nations).
Geopotential determines the vertical distribution of oceanic water masses in oceanography and marine geology. This can be done by collecting observations from several vessels and calculating sea levels at their current locations. The height of each vessel above sea level can then be used to determine the water’s geopotential height as measured along an imaginary line over the Earth’s surface.
Conclusion
To conclude, geopotential is the amount of work it takes to raise a unit mass from sea level at a given altitude to that height against the Earth’s gravitational field. The geopotential surface is an idealised planetary surface that describes the sea level between two known points and allows the calculation of heights at another point anywhere on Earth.
The concept and measurement of geopotential height is an integral part of a geodetic network. One common misconception about measuring heights using a geodetic network is measuring the landscape and calculating elevations using specific formulae. When in fact, it measures both geography and location.
 Profile
Profile Settings
Settings Refer your friends
Refer your friends Sign out
Sign out




