Magnetism, as we all know, is concerned with the interaction of moving charges. Magnetism is a property of the combined electromagnetic force. Diamagnetism, paramagnetism, Ferromagnetism, Anti-ferromagnetism, and Ferrimagnetism are the five forms of magnetism. In this essay let us explain in full ferromagnetism.
Definition
Ferromagnetism is a physical phenomenon (long-range ordering) in which certain materials, such as iron, are attracted to one another strongly. Rare earth minerals and gadolinium contain ferromagnets. Magnetism in magnets is caused by one of the most prevalent phenomena experienced in everyday life.
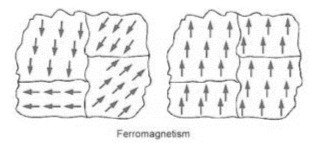
One of the most significant features of ferromagnetic materials is the presence of persistent magnetic moments in ions and atoms. Permanent magnetic moments are found in some ions and atoms, which can be thought of as a dipole with a north pole and a south pole.
If there was a large atomic magnetic moment, some degree of dipole alignment could be seen. This type of magnetic arrangement can be found in some elements such as iron, cobalt, nickel, and their alloys.
Definition of anti-ferromagnetism
Anti-ferromagnetism is a form of magnetism in solids in which neighboring ions that behave like tiny magnets spontaneously align themselves into opposing, antiparallel configurations throughout the material at relatively low temperatures, resulting in a material with essentially no gross outward magnetism.
The table below shows the Neel temperature of an antiferromagnetic material.

Ferromagnetism’s Characteristics
🡪A ferromagnetic material rod can swiftly reorient itself in the magnetic field’s direction.
🡪Even in the absence of a magnetic field, ferromagnetic materials retain their magnetism.
🡪When ferromagnetic materials are heated to high temperatures, the ferromagnetic materials become paramagnetic materials.
🡪Permeability is greater than 1 in ferromagnetic materials.
🡪In gases and liquids, the ferromagnetic mechanism is missing.
🡪Magnetization intensity (M), magnetic susceptibility (xm), relative permeability (µr), and magnetic flux density (B) of ferromagnetic materials are always positive.
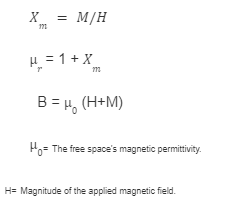
Causes which affects the ferromagnetism
>>The interaction between the alignment of permanent dipoles in atoms and the surrounding atomic dipoles is the primary cause of ferromagnetism.
>>Without the presence of an external magnetic field with a net magnetic moment, domains in a ferromagnetic substance are orientated in the same direction.
>>The magnetic moments of adjoining domains are oriented in opposite directions.
>>As a result, they cancel each other out, resulting in the material’s net magnetic moment being zero.
>>The material is strongly magnetised in a parallel direction to the magnetising field because those domains align themselves in the direction of the external magnetic field.
Ferromagnetism’s Applications
Ferromagnetic materials have a wide range of uses in magnetic storage, electrical, and electromechanical systems.
>Permanent Magnets: Because their magnetism lasts longer, ferromagnetic materials are frequently employed to make permanent magnets.
>>Because of its strong magnetic induction, ferromagnetic materials are appropriate for manufacturing the transformer core and choke, which are subjected to very rapid cyclical changes.
>>Magnetic Tapes and Memory Storage: It will function as a memory storage device. A magnet’s magnetization is determined by the magnetization field and the magnetization cycle it has gone through. As a result, the specimen’s magnetization value is determined by the number of magnetization cycles it has undergone.
Ferromagnetism Examples
Aside from metallic alloys, rare earth magnets are classified as ferromagnetic materials.
The oxidation of iron into an oxide produces magnetite, a ferromagnetic substance.
A refrigerator magnet, which is used to hold notes on a refrigerator door, is a frequent example of ferromagnetism.
conclusion
Ferromagnetism is a physical phenomenon in which some materials, such as iron, have a significant attraction to one another.
Rare earth minerals and gadolinium contain ferromagnets.
Even in the absence of a magnetic field, ferromagnetic materials retain their magnetism.
The interaction between the alignment of permanent dipoles in atoms and the surrounding atomic dipoles is the primary cause of ferromagnetism.
Ferromagnetic materials have a wide range of uses in magnetic storage, electrical, and electromechanical systems.
The oxidation of iron into an oxide produces magnetite, a ferromagnetic substance.
 Profile
Profile Settings
Settings Refer your friends
Refer your friends Sign out
Sign out




