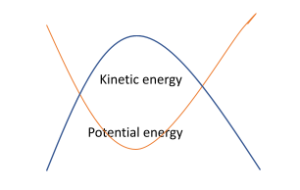
During simple harmonic motion, energy is constantly exchanged between two forms: kinetic and potential.
The potential energy could be in the form of:
- Gravitational potential energy (for a pendulum)
- Elastic potential energy (for a horizontal mass on a spring)
- Or both (for a vertical mass on a spring)
Speed v is at a maximum when displacement x = 0, so:
The kinetic energy is at a maximum when the displacement x = 0 (equilibrium position).
Therefore, the kinetic energy is 0 at maximum displacement x = x0, so:
The potential energy is at a maximum when the displacement (both positive and negative) is at a maximum x = x0 (amplitude).
A simple harmonic system is therefore constantly converting between kinetic and potential energy.
When one increases, the other decreases and vice versa, therefore:
The total energy of a simple harmonic system always remains constant and is equal to the sum of the kinetic and potential energies
The kinetic and potential energy of an oscillator in SHM vary periodically
The key features of the energy-time graph:
- Both the kinetic and potential energies are represented by periodic functions (sine or cosine) which are varying in opposite directions to one another
- When the potential energy is 0, the kinetic energy is at its maximum point and vice versa
- The total energy is represented by a horizontal straight line directly above the curves at the maximum value of both the kinetic and potential energy
- Energy is always positive so there are no negative values on the y axis
Note: kinetic and potential energy go through two complete cycles during one period of oscillation
This is because one complete oscillation reaches the maximum displacement twice (positive and negative)
The key features of the energy-displacement graph:
- Displacement is a vector, so, the graph has both positive and negative x values
- The potential energy is always at a maximum at the amplitude positions x0 and 0 at the equilibrium position (x = 0)
- This is represented by a ‘U’ shaped curve
The kinetic energy is the opposite: it is 0 at the amplitude positions x0 and maximum at the equilibrium position x = 0
- This is represented by an ‘n’ shaped curve
- The total energy is represented by a horizontal straight line above the curves
Average kinetic energy and potential energy of a SHM
The total energy in SHM is given by,
E=12mω2A2
where A is the amplitude and remains conserved.
E=K + U
Kavg=Uavg=E2=14mω2A2
Note:
Average kinetic energy can also be found using
Kavg=1T0TKdt
Average potential energy can also be found using
Uavg=1T0TUdt
Use the relation between restoring force and potential energy
Restoring force is given by:
F=- d Ud X
It is often useful to find the equation of SHM.
Example:
A particle of mass 10 gm is placed in a potential field given by V=(50x2+100)J/kg. Find the frequency of oscillation in cycle/sec.
Solution:
Potential Energy U=mV
U=10-250x2+100
F=- d Ud X=-(100x)10-2
m2x=-(10010-2) x
1010-32x=-10010-2x
2=100, =10
f= 2=102=5
Relation between restoring torque and potential energy
Restoring torque of an SHM can be found by:
=-dUd
It is often useful in finding the equations of SHM and helps in solving problems.
Potential energy per unit length at a given point in a travelling sound wave
Potential energy per unit length (w) at a point is defined as:
w=pvc
p is the sound pressure.
v is the particle velocity in the direction of propagation.
c is the speed of sound.
EXAMPLE
Kinetic energy per unit length at a given point in a travelling sound wave
The Kinetic Energy of a travelling sound wave is defined as:
CONCLUSION
The key ingredient in performing work is energy, which is a quantitative feature of matter. The ability to work is defined as energy. For many sorts of motions, energy is the fundamental unit. Deformations can also be caused by energy, depending on its intensity. “Energy cannot be generated or destroyed, but it can be converted from one form to another,” according to the laws of conservation of energy. The Joule is the international system of energy measuring units.
SHM stands for Simple Harmonic Motion, which is described as a motion in which the restoring force is proportional to the body’s displacement from its mean position. SHM is a type of oscillation in which motion is carried out in a straight line between two extreme points. In SHM, a restoring force is shown pointing toward the mean position or the equilibrium position. In simple harmonic motion, the mean position is a stable equilibrium.
 Profile
Profile Settings
Settings Refer your friends
Refer your friends Sign out
Sign out