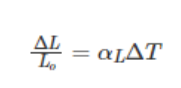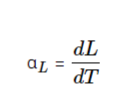Whenever a body undergoes temperature changes, it witnesses a change in height, width, length or volume of material. Although the atoms are firmly packed in solids, the thermal expansion is evident. Consequently, there is a potent balance between the coherent forces possessing the molecules or atoms and the situation it creates.
The coefficient of thermal expansion is the tendency of the subject matter to bring such changes when the temperature changes. This phenomenon is observed in three different forms, i.e., liquid, solids and gases. In such a situation, a body or any object witnesses certain changes in heat regulation expressed as fractional change.
Thermal Expansion
The volume of the material increases with an increase in temperature. This is called thermal expansion. It is the fractional change in length or volume with the change in temperature. In such a situation, the solid expansion employs the coefficient of thermal expansion.
The solid thermal expansion expresses itself in terms of change in length, thickness, and height. The liquid and gaseous forms and the volume expansion coefficient are more useful. It means if the volume of the material is fluid, it can be defined in terms of a volume change.
Coefficient of Thermal Expansion
The solid materials expand on the application of heat and contract when they are cool. It is generally defined as a fractional increase in length per unit following the temperature rise. Although, the exact definition for the concept depends on whether the change in temperature is precise or changes with time.
The true coefficient of thermal expansion relates to the length’s slope tangent, whereas the mean coefficient of thermal expansion governs the cord’s slope between two curved points. Thus, there is a variation in the coefficient of thermal expansion values.
Coefficient of Thermal Expansion Formula
The coefficient of thermal expansion formula is the tendency of an object to bring a certain change in its dimension of length or volume in response to the application of heat. As the heat increases, the kinetic energy of the material also increases. The general formula for the coefficient of thermal expansion is as follows:
ΔL = αLLΔT
Here, αL is the thermal expansion. L is a particular length measurement.
ΔL is the change in length, and ΔT is the temperature change.
Types of Coefficient of Thermal Expansion and Their Formulas
There are three formulas for the coefficient of thermal expansion based on the changes in temperature, i.e., linear expansion, volume expansion, and area expansion.
- Linear expansion – Expansion means an increase or change in length. An increase in length over the dimension of a specific volume is known as linear expansion. Such expansions occur due to a temperature change. The temperature change affects the rate of expansion. It describes how long an object or substance can sustain its original size and shape within the context of heat radiation. This length change occurring due to heat is called linear expansion. The formula for linear expansion is as follows:
- In this formula, L0 is the original length, L is an expanded length, αL is the length expansion coefficient, ΔT is the temperature difference, and ΔL is the change in length.
The coefficient of linear expansion formula describes the rate of change in unit length per unit degree of the temperature change. The formula for the equation can be given as follows:
In this formula, T is the coefficient of linear expansion; dL is a unit change in length; and dT is a unit change in temperature. Thereby, the formula is called the coefficient of linear expansion.
- Volume expansion– An increase in the volume of solid substances due to heat is known as volume expansion.
The change in temperature of ∆T results in the change in the volume of a solid. The equation can be given as follows:
The mathematical formula for the coefficient of volume expansion is as follows:
Here, V0 is the original volume of the solid substance, V is the expanded volume of the solid, αV is the volume expansion coefficient, ΔT is the difference in the temperature, and ΔV is the change in volume of the solid after the expansion.
- Area expansion – An increase or expansion in the area following an increase in temperature is known as area expansion. The area expansion takes place in both the length and width of an object. The mathematical formula for the equation is as follows:
ΔA / A =αa ΔT
In this formula, the αa is the coefficient of area expansion.
The coefficient of area expansion is the degree of area expansion divided by the temperature change. It means a change in the temperature brings an increase in the area of the object. Such a situation denotes αa. It varies based on the temperature.
Conclusion
The coefficient of thermal expansion is the capacity of a certain object or substance to change based on changes in temperature. It is measured by the displacement and temperature samples in a thermal cycle. The linear coefficient expansion , volume coefficient expansion, and area expansion show different responses based on temperature change. The coefficient of thermal expansion units is defined by the fractional change as per the increase in its length per unit whenever the thermal expansion occurs.
 Profile
Profile Settings
Settings Refer your friends
Refer your friends Sign out
Sign out