Resistivity is based on the type of materials used to conduct electricity. From plastics and metals to fluids, every material has some resistance to the current flow. It is an informative quantity that can be used to determine moisture content, dissipation factors and dielectric breakdown of a material. Higher the resistivity, lower the conductance. It happens because there is resistance to the flow of electrons responsible for the current flow in an electric circuit. Several materials have different resistivity, depending on their composition. The letter rho or ρ represents it.
Definition of Resistivity
Electrical resistivity is an intrinsic property of all physical materials that are reciprocal to electrical conductivity. Generally, resistivity can be considered the ability of any material to resist current in the circuit. It basically describes the material and whether it can be an insulator or conductor.
Examples of Resistivity
We have listed down the values of resistivity of different materials.
- Aluminium 2.8 x 10-8
- Bismuth 1.3 x 10-6
- Cadmium 6 x 10-8
- Platinum 0.98 x 10-7
- Antimony 3.9 x 10-7
- Cobalt 5.6 x 10-8
- Gold 2.4 x 10-8
- Copper 1.7 x 10-8
- Germanium 4.6 x 10-1
- Carbon 1 x 10-5
(Graphite)
- Lead 1.9 x 10-7
- Iron 1.0 x 10-7
- Nichrome 1.1 x 10-6
- Manganin 4.2 x 10-7
- Palladium 1.0 x 10-7
- Nickel 7 x 10-8
Formula of Resistivity
Let us learn the formula of resistivity as it makes an easy understanding of the capacity of a material to pass electrons. The formula of resistivity is:
ρ = E/J
Where,
- Resistivity is denoted by ρ
- The magnitude of the electric field is denoted by E
- The magnitude of the density of current is denoted by J
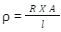
Where,
- The resistivity of the material is denoted by ρ
- The electrical resistance of a conductor is denoted by R
- The cross-sectional area is denoted by A
- Length of the material is denoted by l
It also can be understood by an example. Suppose you have a single wire or a conductor of length l and cross-sectional area A. The resistance of this conductor could be taken as R. According to Ohm’s law, V = IR. Now, take another wire and join it in series to the previous one. The second wire also has length l and area A.
Therefore, the total resistance in series combination can be written as:
R+R = 2R
Also, total length is L+L = 2L
So, when the length increases, resistance increases. In contrast, when wires are connected parallel, the overall length remains the same, but resistance and area change.
Also, the total area of the conductor becomes A+A = 2A.
R is inversely proportional to the cross-sectional area of a material.
From the above observations, we can assume that R ∝ l /A
When we remove the sign of proportionality in the equation, a constant ρ or resistivity comes into the formula.
R = ρ × l /A
Unit of Resistivity
The SI unit of resistivity is Ωm and the CGS unit is Ωcm. By putting the units of length, area and resistance in the resistivity formula, you can derive the resistivity units.
Factors Affecting Resistivity
The resistivity of a specific material depends on various factors such as its age, hardening, temperature, mechanical stressing and alloying. In a semiconductor, the composition and doping of the elements used determines the resistance it will offer. Also, when the temperature increases, the resistivity of a pure conductor increases.
Conclusion
In simple terms, resistivity defines the magnitude of resistance a conductor, semiconductor and insulator will produce during the current flow. Therefore, it can be called an opposite property to that of conductivity. It’s essential to learn about the formula, specific units and other details about this property of a material. This is because it plays a role in electrical devices.
 Profile
Profile Settings
Settings Refer your friends
Refer your friends Sign out
Sign out



