Phosphoric acid, commonly known as orthophosphoric acid, is classified as a weak acid. H3PO4 is its chemical formula. Orthophosphoric acid is the IUPAC designation for phosphoric acid. The prefix ortho- is introduced to distinguish the acid from other phosphoric acids that are linked to it (also called polyphosphoric acids).
When pure, phosphoric acid (H3PO4 ) is solid at room temperature and non-toxic. An 85 percent liquid solution of orthophosphoric acid is the most common type. In nature, the solutions are non-volatile, odourless, and colourless.
What is phosphoric acid?
Phosphoric acid is a phosphorus-containing inorganic acid that is colourless and odourless. Phosphoric acid is a divalent cation sequestering agent that binds to Fe²+, Cu²+, Ca²+, and Mg²+. Phosphoric acid is used as an etching solution in dentistry and orthodontics to clean and roughen the surfaces of teeth prior to the placement of dental equipment or fillings. Furthermore, phosphoric acid is a component of bone and teeth and is involved in a variety of metabolic activities.
Structure of phosphoric acid
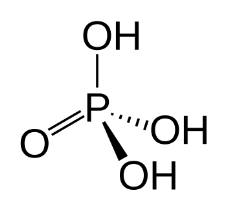
Phosphoric acid is an acid with four oxygen atoms, one phosphorus atom, and three hydrogen atoms.
Properties of phosphoric acid
Physical properties- Pure phosphoric acid is a white crystal-like material with a melting point of 42.35 degrees Celsius. It is a colourless, viscous, odourless liquid with a density of 1.885 g/mL when it is less dense. It is naturally non-toxic and non-volatile. In H2O water, the most widely utilised phosphoric acid content is 85 percent.
Chemical properties
Phosphoric acid is made up of three acidic and replaceable hydrogen atoms. As a result, it reacts differently than other mineral acids. It can react with bases to form three types of salts, such as Na2HPO4, NaH2PO4, and Na3PO4, by substituting one, two, or three hydrogen atoms.
Phosphoric acid molecules can react and mix at high temperatures to form dimers, trimmers, and even lengthy polymeric chains or series, such as metaphosphoric acids and polyphosphoric acids.
2H₃PO₄ → H₄P₂O₇ (anhydride of phosphoric acid)
Uses of phosphoric acid
Some common uses of this acid in different fields are as follows-
- Acids such as phosphoric acid, which is a kind of acid, are widely used to eliminate rust from metals such as iron or steel.
- There are several food additives that include phosphoric acid. This acid is found in a variety of foods, including jams, cereal bars, processed meats, cheese, and other dairy products. It serves as an acidity regulator. In the beverage business, phosphoric acid is utilised as an acidulant to balance pH levels.
- Phosphoric acid is a chemical compound that is utilised in the production of a broad variety of personal care products. Cleaning goods, bath products, perfumes, hair care products and colours, nail products, cosmetics, and other skin care items are just a few of the many categories available.
- This acid is largely employed as a pharmaceutical intermediary in the pharmaceutical industry. Phosphoric acid is used in a variety of applications, with dentistry being one of the most frequent. Teeth cleaning and etching solutions are two of the most prevalent applications of sodium hydroxide.
Phosphoric Acid Hazards
Generally speaking, phosphoric acid is non-poisonous and does not cause harm to the skin or any other part of the body when used in low doses. Even at larger concentrations, it poses a threat to health since it may cause severe skin irritation and even damage to the eyes. When H3PO4 vapours are inhaled, it may also induce disturbances in the respiratory system, which can be fatal. It is thus necessary to store this acid in a metallic or covered fibreboard container (with a polyethene internal bundle) that is maintained in a cold and well-ventilated environment at all times.
what is phosphoric acid
Phosphoric acid is a colourless and odourless crystalline liquid that has a crystalline structure. It imparts a tangy taste to soft drinks while also inhibiting the development of mould and germs, which can readily flourish in a sugary solution, according to the manufacturer. The majority of the acidity in soda is likewise derived from phosphoric acid.
Conclusion
Despite the fact that phosphoric acid is a weak acid, its liquid form is unpleasant to be around in large quantities.
Divalent cations are more readily bound when a sequestering agent is used, which is why it is beneficial. In the fields of dentistry and orthodontics, phosphoric acid is most often used as a cleaning agent. Besides the domains of chemistry and biology, phosphoric acid may also be found in the fields of biochemistry and biogeochemistry.
 Profile
Profile Settings
Settings Refer your friends
Refer your friends Sign out
Sign out




