There are two major types of chemical bonds that can be observed between atoms in a covalent compound. The sigma bond and the pi bond are the two types of bonds. A single bond is always referred to as a sigma bond. A double bond is made up of two bonds: the sigma bond and the pi bond. Both types of bonds, on the other hand, are formed as a result of the overlapping of atomic orbitals. The terms hyperconjugation and resonance are used to describe two methods of stabilising a molecule that are involved in the process. When comparing hyperconjugation and resonance, the most significant distinction is that hyperconjugation involves the interaction between a sigma bond and a p orbital or a pi bond, whereas resonance involves the interaction between pi bonds.
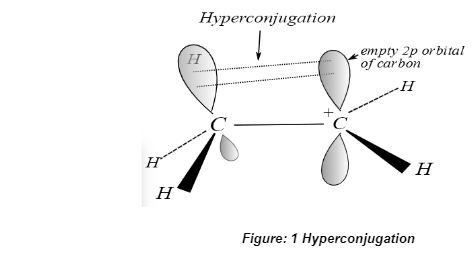
Hyperconjugation
In organic chemistry, hyperconjugation refers to the stabilisation effect that occurs when two sigma bonds interact with one another and one with a pi bond, respectively. Specifically, a sigma orbital will interact with an adjacent empty p orbital, partially filled p orbital, or a pi orbital if they are all adjacent. This interaction is a result of the orbitals overlapping with one another. As a result, an extended molecular orbital is formed, which provides more space for the bonding electron to exist. The repulsion forces between electrons are then reduced as a result. As a result, the molecule is able to maintain its stability. It is usually the case that hyperconjugation occurs due to an overlap in the orbital spacing between bonding electrons of the C-H sigma bond and the 2p or pi orbital of the carbon to its left or right.
The length of a chemical bond is affected by the hyperconjugation of the bond. A sigma bond between two atoms is typically longer than a pi bond between the same two atoms, and vice versa. The length of the sigma bond is reduced as a result of hyperconjugation, while the length of the pi bond is increased as a result. Furthermore, it contributes to the increase in the stability of a carbocation.
Resonance
When bonding electrons in the pi orbital delocalize, a molecule becomes more stable, which is known as resonance stabilisation. The fact that electrons are not fixed in their positions within an atom or a molecule means that they are free to move around. Because of this, it is possible to move lone electrons and pi bonding electrons between different positions in order to achieve a stabilised state. This is referred to as resonance. When attempting to determine the most stable form of a molecule, we employ resonance structures, which display all of the possible structures that a given molecule can take on.
The same number of electrons and the same molecular formula are found in both resonance structures. In addition, the hybridization of atoms in the molecule should be the same in every resonance structure, as should the number of lone pairs in each structure.
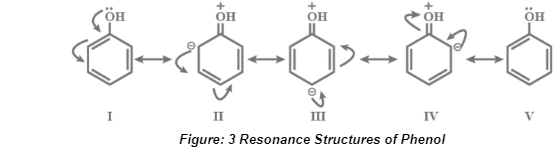
Resonance Structures of Phenol
Phenol’s resonance structures are represented in the image above in their entirety. The original structure of the phenol molecule has been revealed at the conclusion of the study of resonance structures. In this case, it indicates that the real molecule does not contain any pure double bonds at all. Instead of three double bonds, there is a pi electron cloud present. As a result, resonance provides an intermediate structure between two different resonance structures.
Conclusion
Hyperconjugation is an extension of resonance in that both methods result in the stabilisation of a molecule through delocalization of electrons; however, hyperconjugation results in the delocalization of sigma bond electrons in addition to pi bond electrons, whereas resonance results in the delocalization of pi orbitals only.
 Profile
Profile Settings
Settings Refer your friends
Refer your friends Sign out
Sign out




