Introduction:
The indicator phenolphthalein is often used in acid–base titrations. For this purpose, it turns colourless in acidic solutions and pink in basic solutions. It’s a phthalein dye, which means it’s a type of dye.
Phenolphthalein is water-insoluble and is normally dissolved in alcohols before being used in investigations. It’s a weak acid with a tendency to lose H+ ions in solution. The colourless non-ionised phenolphthalein molecule and the fuchsia double deprotonated phenolphthalein ion Further proton loss happens slowly at higher pH levels, resulting in a colourless form. Due to sulfonation, the phenolphthalein ion in concentrated sulfuric acid turns orange red.
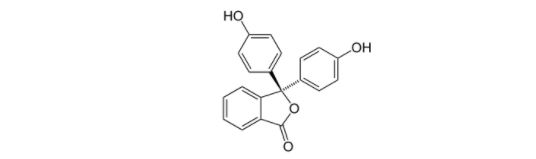
Phenolphthalein structure :
C20H14O4 is the molecular formula for phenolphthalein.
Phenolphthalein has three hexagonal structures, one pentagonal structure, two alcoholic groups, and one ketone group in its structure.The structure of phenolphthalein also includes carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen chains.
Phenolphthalein test :
It’s an organic component that we utilise to determine if something is acidic or basic. Furthermore, in basic solution, the chemical is pinkish, whereas in acidic solution, it is colourless.
Because it does not dissolve well in water, alcohol titration is commonly used to prepare this solution. Furthermore, when a drop of acidic indicator is added to the acid, a white cloud can form.
It’s a solid Phenolphthalein precipitate that occurs when local concentrations are higher than the solubility product. Furthermore, it vanishes when the solution is shaken.
Furthermore, when it comes into touch with a substance with a pH of 8.2, it turns pink, and at a higher pH, it turns purple. Furthermore, ionisation alters the charge and structure of the Phenolphthalein molecule, resulting in a shift in colour. Furthermore, when exposed to an alkaline material, they generate a pink to purple tint.
Working of Phenolphthalein indicator:
For identifying acid and base, the pH scale contains markings ranging from 0 to 14. Furthermore, all acids exist between 0 and 6.9, and the lower the number of acids, the more acidic they are. While pH 7 is neutral, it is the same as the pH of water.
Furthermore, the total base ranges from 7.1 to 14, and the larger the number of bases on a pH scale, the more basic they are. Furthermore, chemists frequently employ litmus paper to determine the pH of a chemical.
The litmus paper, for example, turns red when it comes in contact with acid and blue when it comes into contact with the base.
Phenolphthalein is colourless by nature and acts in a different way than litmus paper. It also becomes pink when exposed to an alkaline solution or base.
Furthermore, the molecule is colourless in acids but begins to turn pink at pH 8.2 and turns brilliant purple in strong bases.
Concrete carbonation of Phenolphthalein :
Concrete, which has a naturally high pH due to the calcium hydroxide created when Portland cement reacts with water, is another application of phenolphthalein’s pH sensitivity. When concrete reacts with carbon dioxide in the air, the pH drops to 8.5-9. When a 1 percent phenolphthalein solution is added to ordinary concrete, it shines bright pink. However, if it remains colourless, it means the concrete has been carbonated. In a similar application, phenolphthalein can be found in certain spackling used to repair drywall holes. The basic spackling ingredient has a pink tinge when applied; however, once the spackling has been cured by reacting with carbon dioxide in the air, the pink colour vanishes.
Phenolphthalein uses :
- As an indicator in acid-base titrations.Titration is a procedure that involves applying the volume of one solution concentration to the volume of another solution. The majority of titrations are acid based.
- The Kastle–Meyer test is a blood test first established in 1903 in which phenolphthalein is used to identify the existence of haemoglobin in the human body; because of the phenolphthalein, it turns pink instantly when peroxide is added.
- Phenolphthalein is found in a variety of toys, including vanishing inks and colours for Barbie’s hair. Sodium hydroxide, which reacts with carbon dioxide, was added to the ink. As hydrogen ions are liberated by the process, the pH drops below and the hue changes.
OH−(aq) + CO2(g) → CO32- (aq) + H+(aq)
Change of colour of phenolphthalein:
In solution, phenolphthalein is weak and colourless, and its ion is pink. The process that causes the colour of Phenolphthalein to change is known as ionisation. Ionisation occurs when one molecule loses or gets an electron, resulting in a negative or positive electric charge for the molecule. The ionised molecule attracts and repels other molecules with the same charge, and it also modifies the molecule’s form.
When all hues of light flow through a phenolphthalein, it appears colourless, but when exposed to an alkaline solution, it blocks the clue colour light and turns pink. The stronger the alkaline solution, the more Phenolphthalein molecules change and the darker the colour appears.
Conclusion:
Incomplete and infrequent bowel movements are treated with phenolphthalein. It is used to empty the bowels in such instances. As a result, it is classified as a laxative. Constipation is treated using this medication. This drug is also utilised in the assessment of renal blood flow to help determine renal function. As a result, phenolphthalein is used as a diagnostic tool.
 Profile
Profile Settings
Settings Refer your friends
Refer your friends Sign out
Sign out



