Mendeleev Periodic Table – As we all know, our periodic table contains 118 elements. 94 of these 118 elements are natural, while 24 are synthetic. Only 30 elements were known in 1800. With the discovery of new elements, scientists found it difficult to memorise the elements and their properties. They began collecting data on the elements and classifying them. The tabular classification of elements according to their qualities became widespread. The periodic table is a tabular arrangement in which various elements are grouped according to their properties.
History of Periodic Table
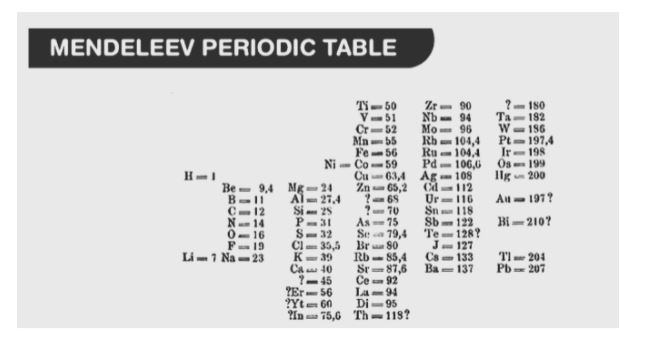
The Mendeleev Periodic Table was created in 1869, following the rejection of the Newlands Octave Law. Mendeleev’s periodic table was organised according to the fundamental property, the atomic mass, and the chemical properties of the elements it contained. Only 63 elements were known at the time of Mendeleev’s research. Mendeleev discovered, after analysing the properties of each element, that the properties of elements were connected to atomic mass in a periodic manner. In order to ensure that elements with similar qualities were grouped together in the same vertical columns of the periodic table, he ordered the elements in a specific way.
Mendeleev considered the formulae of hydrides and oxides to be one of the most fundamental criteria for categorization when it came to chemical qualities. He made a deck of 63 playing cards, on which he wrote the properties of one element on each card. He categorised the elements based on their common characteristics and pinned them to the wall. He discovered that elements were grouped in increasing order of atomic mass and that atoms with comparable qualities recurred on a regular basis in the universe.
Mendeleev’s Periodic Law & Terminology
Mendeleev has stated the following law for the periodic table –
“The properties of elements are a periodic function of their atomic masses,” according to the definition.
- Periodic Table – A chart or table of elements where they have similar chemical properties and physical properties are placed in groups (vertical columns)
- Periodic – Those elements that have the same properties are repeated after a given period of time
- Groups – The vertical rows of elements that are situated in the periodic table are called groups
- Period – The horizontal rows of elements present in the periodic table are called the period
Read more:
Significance of Periods in a Periodic Table
Periods are the horizontal rows that go across the page. During the formation of an atom, periods are defined as the relationship between orbitals, or the likely places in which electrons will be found, within the outermost shell of the atom. Successful periods down the table correspond to atoms having a more electron-rich core of inner shells, as shown by increasing electron density
Advantages of Mendeleev’s Periodic Table
- The chemical elements were classified on the basis of the fundamentals of their atomic masses and their properties.
- If any inert gas element is discovered later then it could be placed in a separate group.
- This periodic table could accommodate the noble gases when they were found.
- He places the noble gases in different groups because these gases are chemically not reactive.
- If a completely new group of elements (noble gases) were discovered, then it was placed in the form of a separate group in Mendeleev’s periodic table. It did not even disturb the arrangement of the table.
- There are enough spaces left vacant to place the future elements that will be discovered.
Limitations of Mendeleev’s Classification
Mendeleev’s periodic table has the following defects –
- The hydrogen position was not defined.
- For a few cases, he places the elements as their similar properties not in the increasing order of their atomic masses.
- The position of such elements was not justified and they were not given separate places in his periodic table.
- Isotopes were not given separate places in the table while the classification was based on the atomic masses.
- He couldn’t explain the cause of the periodicity.
- Lanthanides and actinides positions were not included in Mendeleev’s periodic table.
- A few of the elements were grouped differently while some different elements were grouped.
Conclusion
The periodic table is considered to be one of the most significant contributions to the discipline of chemistry. It is full of patterns that allow us to gain a deeper understanding of the environment in which we live. We would not have many of the items and medicines available to us today if it were not for it.
 Profile
Profile Settings
Settings Refer your friends
Refer your friends Sign out
Sign out




