The Ellingham diagram is a graph that shows how the stability of a compound is temperature dependent. It was created by a British physical chemist named Harold Johann Thomas Ellingham in 1944. The Ellingham diagram is extremely useful in metallurgy. It helps predict the equilibrium temperature between a metal, its oxide and its reactions with nonmetals like sulphur and nitrogen. It is also key in extractive metallurgy, i.e., the separation of valuable metals from their ores. From the graph, we can estimate the tendency to reduce a metal’s oxides and sulphides.
Features of Ellingham Diagram
A graphical representation of the Ellingham diagram is shown below.
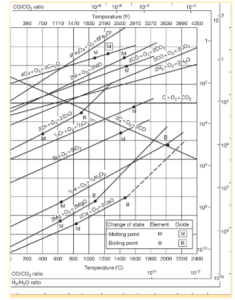 Ellingham diagram is a graphical representation or plot between change in temperature of the system and Gibbs free energy change for a reaction. The reaction is generally the oxidation of metal or reduction of metal oxide. The change in temperature with respect to Gibbs free energy change will be calculated by using the below equation:
Ellingham diagram is a graphical representation or plot between change in temperature of the system and Gibbs free energy change for a reaction. The reaction is generally the oxidation of metal or reduction of metal oxide. The change in temperature with respect to Gibbs free energy change will be calculated by using the below equation:
G = H – TS, where
- H = change in enthalpy of the reaction
- S = change in entropy of the reaction
- T = temperature of the system
- G = change in Gibbs free energy should be negative for a spontaneous reaction
Salient Features of the Ellingham Diagram
- For the formation of metallic oxides, the curves in the Ellingham diagram are straight lines with a positive slope which will be proportional to the change in entropy of the system.
- The lower the line of a metal in the Ellingham diagram, the greater its oxide’s stability. We can gather from the diagram that the stability of an oxide decreases with an increase in temperature.
- If you compare Ellingham diagram curves of two metals at the same temperature, the one with lower Gibbs free energy of oxidation will reduce the oxide with the higher Gibbs free energy of formation.
- If two lines intersect in the Ellingham diagram, it denotes an oxidation-reduction equilibrium.
- If there is a big gap between two lines in the diagram, the effectiveness of the reducing agent of the lower line will be high.
Use of Ellingham Diagram
- The Ellingham diagram is extensively used in the extractive metallurgy industry. This diagram helps select the best reducing agents for a particular metal’s ore.
- It is also used in the purification, extraction and grade setting of steel.
- It is used in the purification of various metals.
Limitations of Ellingham Diagram
The Ellingham Diagram cannot provide reliable information under certain circumstances.
- In this diagram, all the information is based only on the thermodynamic aspect as the graph fully depends on temperature. The graph will not be able to give the kinetic aspect of the reaction, such as the rate of the reaction.
- As we know, the relation between Gibbs free energy and equilibrium constant is represented as:
G = -RTlnK, where
R is the universal gas constant
The graph assumes that all reactants and products are present at equilibrium, which is not always true.
Conclusion
From the Ellingham Diagram, we can analyse the reduction tendency of metals with respect to other metal oxides and oxygen. These graphs are extremely useful for many real-world applications like the extraction and purification of steel and other metals. Though it has several limitations, the graph is an extremely useful tool in extractive metallurgy.
 Profile
Profile Settings
Settings Refer your friends
Refer your friends Sign out
Sign out






