When evaluating and forecasting molecular characteristics and interactions, it’s important to understand periodic trends. Ionization energy, atomic radius, and electron affinity are all examples of common periodic trends. One such tendency is ionic radii, which are closely related to atomic radii. The size of neutral atoms tends to climb down a group and diminish over time. The radius of a neutral atom increases or decreases when it acquires or loses an electron, forming an anion or cation. This module explains why this happens and how it varies from the atomic radii trend.
Ionic Radii
The ionic radius of an atom is determined in a crystal lattice hence the compound must be solid. Depending on the technique, these radii will vary slightly. The radius of an ion is typically calculated via X-ray crystallography.
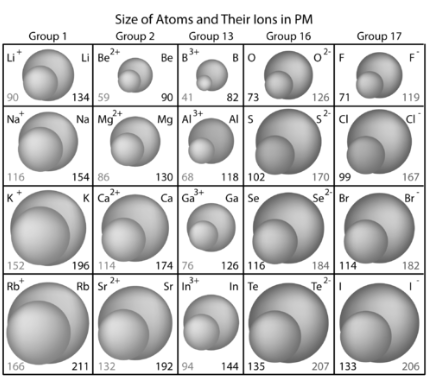
When electrons are removed from an atom, the result is always a cation that is much smaller than the parent atom. The valence electron(s) are eliminated, and the resultant ion has one fewer occupied primary energy level, resulting in a smaller electron cloud. Another reason is that because protons now outweigh electrons, the remaining electrons are drawn closer to the nucleus. The number of electrons ejected is also a consideration. To make the equivalent ion, one electron is lost from the potassium atom, while calcium loses two electrons.
When electrons are added to a parent atom, the result is always an anion that is larger than the parent atom. When the electrons outnumber the protons, the protons’ total attractive attraction for the electrons decreases. Because there are more electrons, there are more electron-electron repulsions, which causes the electron cloud to spread out. It’s worth noting that the ions in group 16 are larger than those in group 17. The anions are formed by adding two electrons per atom to the group 16 elements and one electron per atom to the group 17 elements.
Atomic and ionic radii
The ionic radius of an element differs from its atomic radius. The size of positive ions is less than that of corresponding uncharged atoms. Negative ions have larger atoms than their neutral counterparts.
- Atomic radius, ionic radius, covalent radius, and van der Waals radius are all distinct ways to quantify the size of an atom.
- The atomic radius of a neutral atom is half its diameter. In other words, it is the diameter of half an atom across the outer stable electrons.
- The ionic radius is equal to half the distance between two interacting gas atoms. This number might be the same as the atomic radius, or it could be greater for anions and less for cations, or it could be the same for both.
- Atomic and ionic radius follow the same pattern on the periodic table. Radius decreases as you walk down a group and increases as you move across a period (row) (column).
Ionic radii definition
An ion is an atom that has acquired an electrical charge by gaining or losing one or more electrons. The size of a spherical ion is measured by the ionic radius of the ion (ion) of an atom (either a cation or anion). The ionic radius is comparable to but not identical to the atomic radius, because the ionic size is determined by the distribution of its outermost electrons and is inversely proportional to the ionic effective nuclear charge.
Ionic Radius Group
Why does the radius of a group rise as the atomic number increases? Additional layers of electrons are added as you progress down a group in the periodic table, causing the ionic radius to naturally rise as you move down the periodic table.
Ionic Radius and Period
It may appear odd that the size of an ion shrinks when additional protons, neutrons, and electrons are added over time. There is, however, a reason for this. The ionic radius of metals generating cations diminishes as you progress through a row of the periodic table, as the metals lose their outer electron orbitals. Because the number of electrons exceeds the number of protons, the ionic radius of nonmetals increases as the effective nuclear charge falls.
Shielding and Penetration
Electromagnetic interactions between electrons in an atom change each electron’s effective nuclear charge (Zeff). Penetration is the existence of an electron inside an inner electron’s shell, while shielding is the process by which an inner electron shields an outer electron from the nucleus’ full attractive force, lowering (Zeff). Shielding and penetration are affected by changes in orbital
parameters. Because of their proximity to the nucleus, s-orbital electrons penetrate and shield more effectively than p-orbital electrons within the same energy level (represented by the Principal quantum number, n), while p electrons penetrate and shield more effectively than d-orbital electrons. The size of an ion is determined by shielding and penetration, as well as the effective nuclear charge. The following equation gives an overly basic but useful notion of effective nuclear charge:
Z eff = Z-S
Where
- Z is the number of protons in the nucleus of an atom or ion.
- S is the number of core electrons.
Conclusion
If an atom loses or receives electrons, it forms ions. An atom becomes a cation when it loses an electron and an anion when it gets an electron. The ionic radius is defined as the distance between an ion’s nucleus and the ion’s outermost shell.
In a periodic table, atoms add extra shells (number of electrons) as they move down a group, increasing the ionic radius of the elements.
The ionic radius falls at first, then increases, and then decreases again over time across the period.
 Profile
Profile Settings
Settings Refer your friends
Refer your friends Sign out
Sign out




