Hydrogen is a chemical element with the symbol H and the atomic number 1; its average atomic mass is 1.008amu. In the year 1672, Robert Boyle conducted the first experiment that resulted in the production of this gas. In the year 1766, an English scientist named Henry Cavendish researched its qualities, and Daniel Rutherford found it in the year 1772. Lavoisier termed this gas Hydrogen in 1783. The term comes from the Greek words “hydro” and “genes,” which both indicate “water producer.”
Hydrogen
Hydrogen is the most plentiful element in the cosmos and on Earth. Almost nine out of every ten atoms in the cosmos are hydrogen atoms. Some volcanic gases, as well as the outermost atmospheres of the stars in the universe, contain hydrogen in its free state. Hydrogen atoms make up 90% of total of the universe’s atoms, according to astronomers.
Hydrogen is found in a variety of forms on Earth, mostly in mixture with oxygen in the form of water, and in mixture with carbon, nitrogen, and halogens in the organic form matter in plant and animal tissues, carbs, proteins, and other substances. Coal, petroleum, oil, and natural gas are just a few of the minerals that contain hydrogen. It accounts for 15.4% of the Earth’s crust and seas. The earth’s gravitational force isn’t strong enough to keep light hydrogen molecules in our atmosphere, hence it’s not present there. In crystal rocks, it is ranked eighth in terms of abundance. About 15% of the total of all atoms on the planet are hydrogen atoms.
Properties of hydrogen
It is a colourless, odourless gas having the least density of all gases. It is regarded as the future’s pure fuel, as it is made from water and returns to water when oxidised.
It can be found in water and practically all living organisms’ molecules. It is still held together by carbon and oxygen atoms. It can be claimed that it is the universe’s most plentiful element.
It exists as a gas in the atmosphere at a concentration of one part per million. Hydrogen is a colourless gas that may be produced from a variety of sources, transported, and stored in vast quantities.
Because it holds energy that originated elsewhere, it is called an energy carrier.
In the 16th century, this element was created artificially. It was given the name hydrogen, which means ‘water-former’ in Greek.
Atomic number of Hydrogen
The number of protons in the nucleus of each atom of an element is denoted by its atomic number (represented by the symbol Z). Based only on its atomic number, an atom can be classed as a certain element. Any atom with an atomic number of 8 (with an 8-proton nucleus) is an oxygen atom, while any atom with a different number of protons is a different element.
The number of electrons is equal to the number of protons since atoms are neutral. One electron occupies the region outside the nucleus of all hydrogen atoms. Helium will have two electrons because it has two protons.
Effective atomic number
The overall number of electrons orbiting the nucleus of a metal atom in a metal complex is represented by the effective atomic number (EAN). It is made up of the electrons of the metal atom as well as bonding electrons from nearby electron-donating atoms and molecules. The effective atomic number of the cobalt atom in the complex
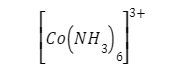
which is the measure of the total of electrons in the trivalent cobalt ion (24) and the numbers of bonding electrons from six surrounding ammonia molecules (2×6=12).
Conclusion
Despite the fact that it is abundant, hydrogen is rarely discovered in its natural state. It is primarily found linked to other elements in chemical compounds. The most common example is water, which has hydrogen linked to the oxygen molecule. It’s interesting to note that when hydrogen is burned, it normally combines with oxygen in the air to generate water.
 Profile
Profile Settings
Settings Refer your friends
Refer your friends Sign out
Sign out




