The process of diazotization is the creation of a diazonium compound or diazonium salt. An aromatic amine combines with the reagent containing a nitrosyl cation (NO) or a reagent capable of creating the matching aryldiazonium salt in an organic reaction. Peter Griess was the first to find it. The method of diazotization is used to make diazonium salts from aromatic amines. Tetrazotization refers to the diazotization of bifunctional aromatic amines (such as benzidine or p-phenylenediamine).
Diazotization Reaction
Aromatic amines create diazonium salts when they react with nitric acid & mineral acids, yielding water as a by – product. The diazotization reaction is the name given to this process.
Reactions in words in can be expressed in the reaction form as;
Mineral Acid + Aromatic Amine + Nitrous Acid → Water + Diazonium Salt
In 1858, Peter Griess, a German industrial chemist, was the first to report such a reaction. He went on to find a slew of other diazonium salt-related reactions.
In most cases, an aromatic amine reacts with nitrous acid in the presence of some other acid to produce these diazonium salts.
Diazotization Reaction Mechanism
Diazotization Reaction Mechanism can be explained in 4 steps;
Formation of Nitronium Ions
Nitric acid forms nitronium ions when it combines with mineral acids (mineral acids give hydrogen ions).
Formation of Nitronium Ions
Formation of N-Nitrosamine
N-nitrosamines are formed when nitrosonium ions combine with aromatic amines. When the nitrosonium ion combines with an aromatic amine, its positive charge is transferred to the aromatic amine’s nitrogen, which only offers the nitrosonium ion a few electrons. Between aromatic amine & nitrosonium ion, a nitrogen-nitrogen bond is created as a result. N-nitrosamines are formed when deprotonation occurs.
Formation of Diazohydroxide by the Protonation & Deprotonation of N-Nitrosamine
N-nitrosamines undergo protonation and then deprotonation. Diazo hydroxides are formed as a result of this process.
Formation of Diazonium Ions by the Protonation of the Diazo Hydroxide
Diazohydroxide is protonated in this stage to produce water & diazonium ions. It is simple to convert diazonium ions to diazonium salts.
Titration of Diazotization
A diazotization reaction or generation of a diazotized salt is used in diazotization titration. The material is initially weighed & placed in the standard Erlenmeyer flask in the diazotization titration process. Fill the flask halfway with distilled water and then add the concentrated HCl and KBr.
This is a tried-and-true solution. Then, for titration, pipette the required amount of the standard solution into some other Erlenmeyer flask. The temperature is regulated between 0 and 5 degrees Celsius. The starch iodide paper is then titrated with the NaNO2 solution till it becomes blue.
Uses or Applications of Diazonium Compound
In the dye & pigment industries, diazonium compounds are quite helpful. Originally, they were employed to create water-fast coloured fabrics.
Diazonium salts are useful in Fischer Indole Synthesis since they can be converted to hydrazine derivatives using stannous chloride.
Diazonium compounds are used as standard reagents in the production of organic molecules.
Diazonium salts have potential to be used in nanotechnology applications. They’re useful for efficiently functionalizing single-walled nanotubes.
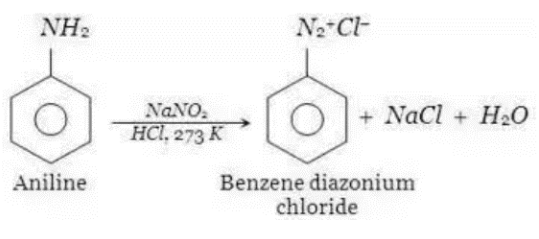
Diazotization Of Aniline
When aniline or Arenediazonium salt combines with a highly reactive chemical like phenol or amines, it forms azo compounds, which are coloured compounds. A coupling reaction is the name given to this type of reaction. In order to make red azo dye, this chemical reaction is used. The introduction of cold aqueous sodium nitrite to the primary aromatic amine in the presence of an acid is typically used to make aromatic diazonium salt. This reaction requires a temperature of 273–278K to take place.
The usage of Diazo compounds or aliphatic Azo is less common than the use of aromatic diazo compounds. As radical initiators, Diazo compounds or aliphatic Azo are utilized. At elevated temperatures, diethyl diazene, an aliphatic azo molecule, cleaves the C-N bond, resulting in the removal of nitrogen gas producing radicals.
Conclusion
Diazotization refers to the chemical process of turning a primary aromatic amine into the equivalent diazonium salt of the amine. Diazotization is another name for this process.
In order to produce the diazonium salt, the diazotization reaction mechanism often requires the use of nitrous acid & another acid in the treatment of the aromatic amines.
Diazonium salts are useful in Fischer Indole Synthesis because stannous chloride can be used to convert them to hydrazine derivatives.
 Profile
Profile Settings
Settings Refer your friends
Refer your friends Sign out
Sign out