Did you ever realise that the artificial sweeteners that you consume as chemicals daily are chemicals themselves?
Under the Food and Drug Administration, food preservatives are included in heavy percentages per cent of the packaged foods we consume today. The problem is that some of these chemicals are highly detrimental to your health, while others are necessary to keep the food fresh and edible. Let us find out more about the chemicals included in the food.
Food Preservatives
All the parts of food in canning food preservation are chemicals. People eat the majority of their food made up of chemicals called carbs, fat, proteins, minerals, and water. The vitamins and natural antioxidants, antimycotics, buffers, thickeners, emulsifiers, chelating agents, colours, and flavours are just a few of the small amounts of other chemicals found in food.
Many chemicals are added critically to make food more appealing and last longer. There are a lot of food additives out there. Still, the main ones are food colours and sweeteners, antioxidants, fat emulsifiers, stabilising agents, flour improvers (like gluten), food preservatives, and nutritional supplements like minerals, vitamins, and amino acids. Only a nutritional supplement has any nutritional value, and nothing else has it. Many types of chemicals listed below are used nowadays as food preservatives.
Food additives
Food additives are food preservatives that are added to improve the look, taste, or even to keep the flavours of the food. Some of them, such as sugar and salt, are naturally occurring flavours. However, chemists have developed many different flavours, and methyl salicylate is one of them.
The following are examples of significant food additives:
- Food colours
- Preservatives
- Enzymes
- Artificial flavours and sweeteners
- Colouring Agent for Food Colorings
The colourant is used as a chemical in food to alter a food substance’s appearance. Colours can be found in nature and those that have been purposefully created. Caramel is an example of a naturally occurring food colour, whereas caramel colouring is an example of an artificially created food colour.
- Preservatives
Antibacterial, antifungal, and antimicrobial preservatives are chemicals used to preserve food against bacteria, yeast, and mould. Both Class-I and Class-II are subdivided into two groups: I and II, respectively. Salt, sugar, and vegetable oils are examples of class-I preservatives. Preservatives belonging to the Class II family are listed below in alphabetical order.
- Sodium benzoate
Sodium benzoate is the widest variety of preservatives used in the food market. It is also the most expensive. It is utilised as a flavouring agent in soft drinks and acidic dishes.
- Sodium metabisulphite
Foods like jams, pickles, squashes, and similar items are preserved with sodium metabisulphite.
- Sorbic acid
Mould and yeast development are inhibited by using sorbic acid and its salts. Sorbic acid is a powerful antifungal agent. A variety of items, including cheese, baked goods, and some meats, are treated to keep yeasts and moulds from growing.
- Enzymes
When it comes to converting processes from one material to another, enzymes are biological catalysts that are utilised. The enzymes participating in a chemical process reduce the energy and time necessary to finish. Food processing companies employ enzymes in manufacturing food preservatives items such as dairy products, fruit juices, beer, bread, and other baked goods.
- Artificial Sweeteners:
Sucrose and fructose are two of the most common natural sweeteners. Many people use artificial sweeteners because they add calories and cause tooth decay. For example, some of them are saccharin, aspartame, alitame, sucralose, cyclamate, and L-glucose.
- Saccharin
It is one of the most widely used sweetening compounds, and it may be found in a variety of items, including beverages, sweets, pharmaceuticals, and toothpaste. However, it has a severe bitter (or metallic) aftertaste at high concentrations 550 times sweeter than cane sugar.

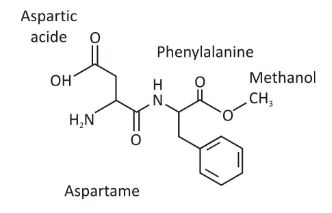
- Aspartame
Sodium aspartate is an amino acid dipeptide created by combining aspartic acid and phenylalanine to form aspartame. It is a non-saccharide sweetener that is around 200 times sweeter than cane sugar in terms of sweetness. A sweet flavour is there, but there is no unpleasant chemical (or) metallic aftertaste that has been seen with other artificial sweeteners.
- Cyclamate
Cyclamate has a sweetness that is approximately seven times greater than sucrose in terms of sweetness. Researchers discovered that the combined sweetness of cyclamate and saccharin (10:1) was si gnificantly sweeter than either of the two substances alone.
- Alitame
Alitamame is an artificial sweetener composed of aspartic acid and alanine as part of a dipeptide bonding. It is thought that the new amine is attached to the alanine moiety of alitame. It is responsible for the increased sweetness and potency of alitame. Compared to sucrose, alitame is approximately 2000 times sweeter and is more stable than aspartame. The sweetness of food is challenging to manage when it is used as an artificial sweetener under the circumstance of high intensity of the sweetener used.

- Sucralose
A trichloro-derivative of sucrose, it is a sweetener used in baking. When cooked at the appropriate temperature, it has the appearance and flavour of sucrose. In addition to being about 600 times sweeter than sucrose, it has no known adverse effects on tooth decay or illness.

Advantages of Food Preservatives
- The nutritional content of food can be improved or maintained by adding certain additions to the recipe.
- Ensures that food remains fresh for significantly more extended periods
- Making seasonal vegetables and fruits available all year long saves time and money.
- Cheaper
- Increase the nutritional value of food, for example, by adding vitamin C to bread.
- For example, using a sweetener instead of sugar can help you consume fewer calories overall.
Disadvantages of Food Preservatives
- ADHD and other behavioural disorders have been linked to this condition.
- An allergic response can occur in certain persons, especially youngsters.
- As of yet, there is no proof that there is a relationship between the two.
- Asthma-related links may hurt specific individuals
- High blood pressure is a problem that may exacerbate.
- In canning food preservation, it is used instead of genuine ingredients. The food is less healthy.
- Calories may be more abundant.
Conclusion:
Chemistry has helped the modern world in a lot of different ways. Food preservatives have made a big difference in eating food every day. They help keep the food safe. Most of the food we buy at the store has a shelf life of a few months to a few years. These foods can only stay fresh because they add these chemicals to prevent spoilage.
 Profile
Profile Settings
Settings Refer your friends
Refer your friends Sign out
Sign out






