Ethanol is an alcohol, often known as ethyl alcohol or drinking alcohol in chemistry. Ethanol could be used as a fuel since alcohol combustion produces heat energy. Ethanol is a clear, colourless liquid with the typical alcoholic scent. Ethanol is largely employed as a solvent in the manufacture of varnishes and perfumes, as well as a biological specimen preservative. Furthermore, ethanol is a disinfectant that can also be eaten as a beverage. Bioethanol (ethanol obtained from biomass) is a gasoline additive or alternative fuel
Chemical Reactivity of Ethanol with Oxygen
Ethanol is used as a flammable fuel. The animation below depicts the net reaction that occurs during the combustion of ethanol. It is important to note that ethanol burning requires the presence of oxygen. While CO2 will eventually be absorbed by plant matter, it will not happen instantly; for more details, see the carbon dioxide atmospheric residence period.
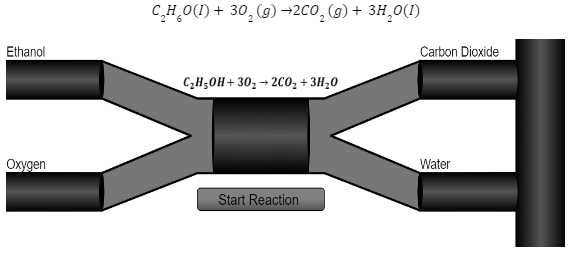
The alcohol combustion reaction is an exothermic event that releases heat energy. A negative enthalpy change ∆H value is also present in the reaction.
Formula of Ethanol
Ethanol is a main alcohol that is ethane with a hydroxyl group replacing one of the hydrogens. It functions as an antiseptic, polar solvent, neurotoxic, central nervous system depressant, teratogenic agent, NMDA receptor antagonist, protein kinase C agonist, disinfectant, human metabolite, Saccharomyces cerevisiae metabolite, Escherichia coli metabolite, and mouse metabolite. It’s an alkyl alcohol, a volatile organic chemical, and a part of the ethanol family. It’s an ethoxide’s conjugate acid.
Molecular Formula: C2H6 or CH3CH2OH
Ethanol and Oxygen
Ethanol: Ethanol, commonly known as ethyl alcohol, grain alcohol, or alcohol, is a member of the alcohols class of chemical substances with the molecular formula C2H5OH. Ethanol is a common industrial chemical that is used as a solvent, like a gasoline additive and in the synthesis of other organic chemicals (forming a mixture known as a gasohol). Ethanol is an intoxicating ingredient found in many alcoholic beverages, including beer, wine, and distilled spirits.
Oxygen: Ethanol is a primary alcohol that is ethane with one of the hydrogens replaced by a hydroxyl group. It’s an antiseptic, polar solvent, neurotoxic, central nervous system depressant, teratogenic agent, NMDA receptor antagonist, protein kinase C agonist, disinfectant, and human, Saccharomyces cerevisiae, Escherichia coli, and mouse metabolite. It’s an alkyl alcohol, a volatile organic molecule that belongs to the same family as ethanol. It’s the conjugate acid of an ethoxide.
Conclusion
The fermentation of carbohydrates (the method used for alcoholic beverages) and the hydration of ethylene are the two basic processes for producing ethanol. Using yeast cells, fermentation is the process of turning carbohydrates to ethanol. Sugar crops like beets and sugarcane, as well as grain crops like corn, are the most common raw materials fermented for the manufacturing of industrial alcohol (maize). The hydration of ethylene is accomplished by passing a mixture of ethylene and a large excess of steam over an acidic catalyst at high temperature and pressure.
Ethanol created from fermentation or synthesis is a dilute aqueous solution that requires fractional distillation to concentrate. Direct distillation can produce a constant-boiling-point mixture with 95.6 percent ethanol by weight at best. Anhydrous, or absolute, alcohol is produced by dehydrating the constant-boiling-point combination. Denatured ethanol for industrial usage is frequently made using methanol, benzene, or kerosene to make it unsafe to drink.
 Profile
Profile Settings
Settings Refer your friends
Refer your friends Sign out
Sign out




