Chemical reactivity of aspirin (A) Aspirin enters cells easily and reacts with a wide range of cellular chemicals. Aspirin, for example, can react with water to produce the hydrolysis byproduct of salicylic acid. Aspirin can also produce acetylated products when it reacts with nucleophilic metabolites (e.g., glutathione) or proteins.
Aspirin has the ability to bind to enzyme active sites and modify nucleophilic functional groups. Aspirin, for example, acetylates SER530 in COX-1, rendering the enzyme inactive.
Aspirin acetylates active site nucleophilic amino acids in this experiment. The proteins are then incubated with activity-based probes to reveal catalytically inactive functional groups within the now-dead enzymes.
In patients undergoing coronary artery bypass grafting, preoperative aspirin administration improves oxygen
Platelet release of thromboxane (Tx) A(2) may be one of several factors responsible for lung injury after cardiopulmonary bypass, resulting in pulmonary vasoconstriction and impaired oxygenation.
Tx receptor inhibition or production improved lung function in experimental models. Aspirin, which is widely used in the treatment of ischemic heart disease due to its antiplatelet activity, is usually stopped a week before the operation to restore normal platelet hemostatic function.
The goal of this study was to see if there was a link between the time of aspirin discontinuation before coronary artery bypass surgery and postoperative oxygenation and bleeding.
Acetylsalicylic Acid (C9H8O4) / Aspirin
Acetylsalicylic acid (ASA) is an irreversible inhibitor of platelet aggregation, but its activity is lost after first-pass deacetylation to salicylic acid (SA). Acetylsalicylic acid was introduced into the pharmaceutical industry more than a century ago. While it was initially thought to be an analgesic, doctors soon discovered that it had a wide range of other medicinal benefits. In 1894, the German chemist Felix Hoffman founded the Bayer Pharmaceutical Company. In search of a medication to alleviate his father’s arthritis pain, he revisited Brugnatelli and Fontana’s salicin, which had been further modified by chemists to produce pure salicylic acid.
Hoffman created acetylsalicylic acid (ASA) by combining salicylic acid with a buffer. This compound was better tolerated and had fewer gastrointestinal side effects. Acetylsalicylic acid was introduced to the market in 1899 and marketed as “aspirin.”
Uses of Aspirin(C9H8O4)
- Acetylsalicylic acid is a cyclooxygenase inhibitor.
- It’s used to keep venous and arterial thrombosis at bay.
- It is employed in the treatment of various types of headaches.
- It is used as an anti-inflammatory agent in both chronic and acute inflammation.
- It is thought to lower the overall risk of developing cancer and dying from it.
- Aspirin is an important part of the treatment of heart attack victims.
- It is a first-line treatment for acute rheumatic fever’s fever and joint pain.
Consideration for Safety
Wear goggles for the duration of this experiment. Salicylic acid, acetic anhydride, and phosphoric acid are used in this experiment. Salicylic acid and aspirin may irritate your skin or eyes, but they are not dangerous. Excessive amounts of these can be discarded in the sink or, if packaged, in the trash. If you spill some, wipe it up with a wet paper towel and discard the towel. Acetic anhydride and sulfuric acid can both cause severe burns.
Only use them in the hood, and make sure the hood fan is turned on! When working with these chemicals, wear gloves. Excess chemicals must be disposed of in the water-filled plastic tub. The acetic anhydride will be converted to vinegar and the sulfuric acid will be diluted as a result.
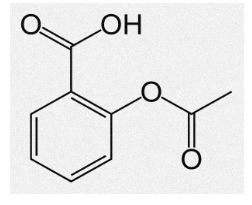
Aspirin Formula and Structure
Acetylsalicylic Acid has the chemical formula C9H8O4. Likewise, the extended formula for the same is CH3COOC6H4COOH. It also has a molecular mass of around 180.159 g mol-1. The same molecule is formed by an aromatic ring with two functional groups in position –orto: carboxylic acid is the first substituent and an ester group is the second.
When it comes to Aspirin’s molecular geometry, it is planar. This is due to sp² hybridization of the phenyl ring and carboxylic groups. The chemical structure of Aspirin is written as follows in the common representations used for organic molecules:
Conclusion
Aspirin enters cells easily and reacts with a wide range of cellular chemicals. Aspirin, which is widely used in the treatment of ischemic heart disease due to its antiplatelet activity, is usually stopped a week before the operation to restore normal platelet hemostatic function. The goal of this study was to see if there was a link between the time of aspirin discontinuation before coronary artery bypass surgery and postoperative oxygenation and bleeding. Acetylsalicylic Acid / Aspirin Acetylsalicylic acid is an irreversible inhibitor of platelet aggregation, but its activity is lost after first-pass deacetylation to salicylic acid. It is employed in the treatment of various types of headaches. It is thought to lower the overall risk of developing cancer and dying from it. Aspirin is an important part of the treatment of heart attack victims. Salicylic acid is reacted with an excess of acetic anhydride to produce aspirin.
 Profile
Profile Settings
Settings Refer your friends
Refer your friends Sign out
Sign out