The term “universal solvent” refers to water’s enormous capacity to dissolve a wide range of molecules, and it is this capacity that makes water such a priceless life-sustaining agent. Water’s function as a solvent aids cells in the transfer and use of chemicals like oxygen and nutrients on a biological level
An overview on Biological Significance
Major biological functions that appear to be shared by all three gases include the control of central nervous system activity and vascular homoeostasis. It is becoming more and more obvious that each gas’s production and biological activity are, to some extent, controlled by the presence of the others. As a result, it is important to think of these molecules working together, rather than individually, to influence cell function. Ammonia, acetaldehyde, sulphur dioxide, and nitrous oxide are further, speculative candidates for gaseous cell signalling chemicals. It is unknown if these chemicals are also involved in controlling how the body works.
The biological significance of water
The term “universal solvent” refers to water’s enormous capacity to dissolve a wide range of molecules, and it is this capacity that makes water such a priceless life-sustaining agent. Water’s function as a solvent aids cells in the transfer and use of chemicals like oxygen and nutrients on a biological level Blood and other water-based fluids assist in transporting molecules to the required regions. As a result, water’s function as a solvent makes it easier for molecules like oxygen to go through the body during respiration and has a significant influence on how quickly medications may reach their intended destinations in the body.
Water Supports Cellular Structure
In biology, water plays a crucial structural role as well. Water physically fills cells to support the maintenance of form and structure. Similar to putting air in a balloon, the water found inside many cells, including those that make up the human body, exerts pressure that opposes outside forces. Even plants that can keep their cell structure intact without water, however, nevertheless need water to exist. Everything inside cells may have the proper molecular form thanks to water. This is also one of the most crucial functions of water since form is essential for metabolic activities.
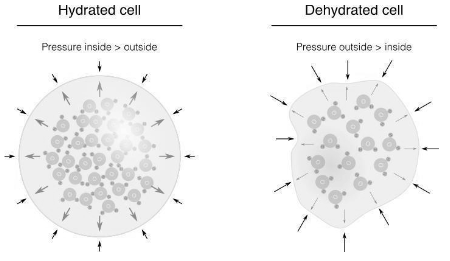
Water also helps to create the membranes that enclose cells. Every cell on Earth is encased in a membrane, the majority of which is made up of two layers of phospholipid molecules. Similar to water, phospholipids are made up of a polar “head” and a nonpolar “tail.” As a result, the polar heads interact with the water, but the nonpolar tails strive to stay away from the water and engage in interactions with one another. Phospholipids naturally form bilayers with the heads pointing outward towards the surrounding water and the tails pointing inward, excluding water, in search of these advantageous interactions. Cells are surrounded by a bilayer that permits certain materials, such as salts and nutrients, to enter and exit the cell.
Chemical Reactions of Water
Numerous chemical activities that create and degrade crucial cell components directly involve water. Water is necessary for photosynthesis, the process by which plants produce the carbohydrates needed by all living things. Additionally, water helps cells create bigger molecules. Proteins and DNA are composed of repeating units of smaller molecules. These tiny molecules combine in the process resulting in the creation of water. In contrast, water is necessary for the process that breaks these molecules down, allowing cells to repurpose small molecules or get nutrients.
Biological significance example
Statistically significant effects that have a notable influence on health or survival are referred to as having “biological significance” (as opposed to statistical significance). Even though an observed impact is not physiologically significant, it may nevertheless be statistically significant if it is modest but very exact (i.e., there is minimal uncertainty in the observed value). For instance,
A factor that lowers blood pressure by 1 mmHg on average can be statistically significant if it is evaluated on a large sample of persons, but a 1 mmHg drop in blood pressure on average has no direct therapeutic use.
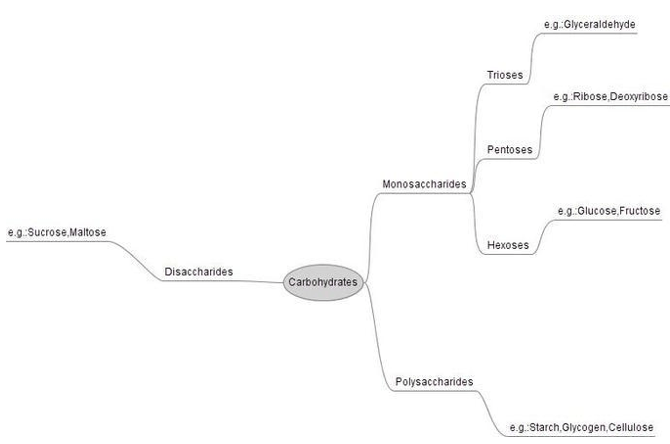
Biological significance of carbohydrates
Large molecules required for life, known as biological macromolecules, are constructed from smaller organic molecules. Carbohydrates, which are further broken down into the three subtypes of monosaccharides, disaccharides, and polysaccharides, are a significant class of biological macromolecules. In truth, we need carbs in our diet; they may be found naturally in grains, fruits, and vegetables. Importantly, carbs give the body energy, especially in the form of glucose, a simple sugar that is a constituent of starch and a component of many staple meals.
Conclusion
As a result, water’s function as a solvent makes it easier for molecules like oxygen to go through the body during respiration and has a significant influence on how quickly medications may reach their intended destinations in the body. Water’s function as a solvent aids cells in the transfer and use of chemicals like oxygen and nutrients on a biological level.
 Profile
Profile Settings
Settings Refer your friends
Refer your friends Sign out
Sign out




