The interatomic linkage that results from the sharing of an electron pair between two atoms is known as a covalent bond in chemistry. The binding is caused by the electrical attraction of their nuclei for the same electrons. When the total energy of the bonded atoms is lower than that of widely separated atoms, a covalent bond is formed.
Bond that is covalent A bond between two atoms in which a pair of electrons are shared. A single line is often drawn between the symbols of the two atoms that have bonded together to represent the bond. Sometimes the bonding occurs between atoms of different elements (for example, hydrogen chloride, H–Cl), and other times it occurs between atoms of the same element for example, fluorine, F–F. Any uncharged particle containing covalently bonded atoms is referred to as a molecule.
Bonds’ polarity. The shared electrons are equally available to each of the atoms in a pure covalent bond. Only when two atoms of the same element bond together does this arrangement occur. As a result, the hydrogen molecule, H2 contains a pure covalent bond.
Covalent Bond Formation
When the difference between the electronegativity of two atoms is too tiny for an electron transfer to produce ions, a covalent bond occurs. Electrons that are shared in the space between two nuclei are known as bonding electrons. The bound pair serves as the “glue” that holds molecular units together.
For example: A single covalent link is created when two chlorine molecules share one pair of electrons.
When two chlorine atoms come close enough to share their valence electrons and create a shared pair of electrons, their valence electrons are shared. Each atom owns an equal portion of the common pair. The two chlorine atoms are connected by a single covalent bond since they only share one pair of electrons.
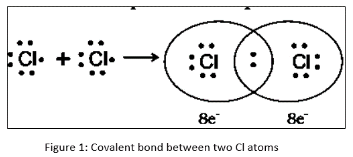
Covalent Bond Properties
- Neutral molecules make compose covalent compounds.
- Water insoluble covalent molecules are soluble in organic solvents.
- In general, covalent compounds have low melting and boiling points.
- Electricity does not conduct through covalent molecules.
There are Numerous Terminologies Used in the Covalent Bond
Compounds
Compounds are defined in chemistry as substances made up of two or more different elements that have been chemically combined. Water and salt are both compounds. The elements sodium and chloride make up salt. These and other elements can be found on the periodic table. They are denoted by the letters Na and Cl, which stand for sodium and chloride, respectively. The compound sodium chloride, represented by the formula NaCl, is formed when sodium and chloride combine.
Properties
Compounds properties given below:
- They come in a variety of shapes and sizes.
- They don’t have any distinct characteristics.
- They can be separated through physical means.
- It has a uniform composition.
- There are only one type of particle in a compound.
- One or more atoms of the same or different elements create a compound.
- A compound’s constituents are present in a specific mass ratio.
- The proportions of the elements in a compound are fixed.
- Compounds have a specific set of characteristics.
- Chemically, compounds can only be broken down.
Molecule
A molecule is a group of two or more atoms bound together by chemical bonds; the term may or may not include ions that meet this condition depending on the context. In quantum physics, organic chemistry, and biochemistry, the distinction between ions and molecules is sometimes omitted, and polyatomic ions are referred to as molecules. The number of atoms that make up a molecule determines the size of the molecule.
The majority of molecules are too tiny for the naked eye to see. With a bond length of 0.74 angstroms, diatomic hydrogen (H2) is the smallest molecule. Nucleic acids, proteins, carbohydrates, and lipids are examples of macromolecules, which are huge molecules made up of smaller subunits. Specialized microscopes can observe certain macromolecules.
Two Atoms
Diatomic molecules have only two atoms, which can be of the same or distinct chemical elements. The prefix di- is derived from the Greek word di-, which means two. If a diatomic molecule has two atoms of the same element, such as hydrogen (H2) or oxygen (O2), it is homonuclear (O2). Two atoms of the same chemical element are not similar. First and foremost, the electrons of an atom can exist in a variety of states. If one copper atom contains an excited electron and the other copper atom has all of its electrons in the ground state, the two atoms are distinct. The excited copper atom emits a small amount of light when the electron relaxes back to the ground state, but the copper atom in the ground state does not.
Conclusion
In this article we learned, a covalent bond is a chemical relationship between two atoms or ions in which the electron pairs are shared. A molecular bond is another name for a covalent link. Covalent bonds are formed when two nonmetal atoms have the same or nearly similar electronegativity values. Because most carbon compounds interact predominantly through covalent bonding, covalent bonds are particularly significant. Covalent bonding allows molecules to share electrons with one another, allowing for the formation of extended chains of compounds and a greater level of complexity in life.
 Profile
Profile Settings
Settings Refer your friends
Refer your friends Sign out
Sign out




