A cycloaddition is a chemical reaction where “two or greater unsaturated molecules (or parts of the identical molecule) integrate with the formation of a cyclic adduct in which there may be a net reduction of the bond multiplicity.” The resulting response is a cyclization response.
The term oxidation turned into initially used to explain reactions wherein an element combines with oxygen. For example- The reaction between magnesium metal and oxygen to shape magnesium oxide includes the oxidation of magnesium.
Cycloadditions
Cycloadditions can be described as the use of two systems of notation. They are reactions in which π bonded molecules come collectively to make a new cyclic molecule with the formation of two new σ bonds. An older however nonetheless commonplace notation is primarily based on the size of linear preparations of atoms inside the reactants. It makes use of parentheses: (I + j + …) wherein the variables are the numbers of linear atoms in every reactant. The product is a cycle of size (I + j + …).
Types Of Cycloadditions
The different types of cycloadditions are discussed below in detail:-
Diels-Alder reactions
The Diels-Alder reaction is perhaps the most critical and normally taught cycloaddition reaction. Officially it is a [4+2] cycloaddition reaction and exists in a large variety of forms, along with the inverse electron-call for Diels–Alder reaction, Hexadehydro Diels-Alder response, and the associated alkyne trimerization. The response can also be run in opposite directions within the retro-Diels–Alder reaction.
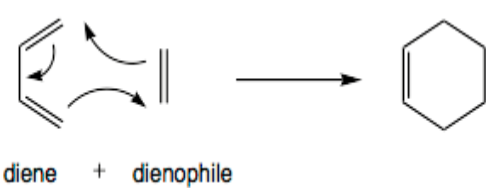
Reactions regarding heteroatoms are acknowledged; inclusive of the aza-Diels–Alder and Imine Diels–Alder response.
1,4 -Cyclohexadienes
1,4-Cyclohexadiene is an organic compound with the formulation C6H8. It’s miles a colourless, flammable liquid that is of an educational hobby as a prototype of a massive magnificence of related compounds referred to as terpenoids, an example being γ-terpinene. An isomer exists of this compound, 1,three-cyclohexadiene.
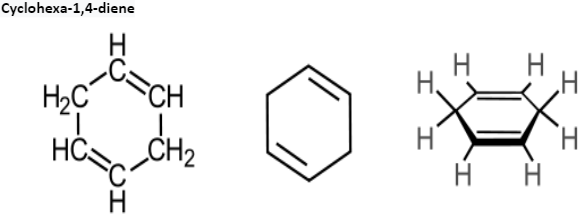
Synthesis and Reactions
Within the laboratory, substituted 1,4-cyclohexadiene is synthesised through Birch reduction of related aromatic compounds using an alkali metal dissolved in liquid ammonia and a proton donor which includes alcohol. In this manner, over reduction to the fully saturated ring is prevented.
1,four-Cyclohexadiene and its derivatives are without difficulty aromatized, the using pressure being the formation of an aromatic ring. The conversion to an aromatic system can be used to trigger other reactions, which include the Bergman cyclization.
Application
Useful for the reduction of radical intermediates formed in electron-switch mediated ring-opening reactions.
1,4 – Cyclohexadiene (1,4 – CHD) was used to have a look at the formation of the parent ion from heavy fragmentation of 1,4 – CHD on irradiation with a high-depth laser pulse.
Oxidation
An older meaning of oxidation becomes while oxygen is changed into delivered to a compound. This was because oxygen gas (O2) turned into the first recognized oxidising agent. Even as the addition of oxygen to a compound usually meets the standards of electron loss and an increase in the oxidation state, the definition of oxidation became elevated to encompass other types of chemical reactions.
A traditional instance of the old definition of oxidation is when iron combines with oxygen to form iron oxide or rust. The iron is stated to have oxidised into rust. The chemical response is:
2 Fe + O2 -> Fe2O3
The iron metal gets oxidised to form the iron oxide which is called rust.
- Oxidation occurs while an atom, molecule, or ion loses one or greater electrons in a chemical reaction.
- While oxidation takes place, the oxidation state of the chemical species will increase.
- In Oxidation, it is not necessary that oxygen is present. In the beginning, the time period was used while oxygen-induced electron loss in a reaction. The cutting-edge definition is extra preferred.
Thus now, oxidation is defined as the loss of electrons during a reaction by a molecule, atom, or ion. Oxidation occurs while the oxidation state of a molecule, atom, or ion is increased. In other words, Oxidation is a method that entails the addition of oxygen or any electronegative element or the removal of hydrogen or an electropositive element.
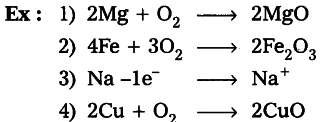
Conclusion
Cycloaddition reactions are taken into consideration as the maximum influential bond forming reactions in organic chemistry due to their capability to generate the multiple C–C in addition to C-heteroatom bonds in a single step.
Whereas the result of oxidation is the lack of electrons or the increment of the oxidation state by way of a molecule. The electrons that are lost by means of a molecule throughout oxidation are gained by a different molecule that gets reduced inside the process.
 Profile
Profile Settings
Settings Refer your friends
Refer your friends Sign out
Sign out




