In the periodic table, f block elements appear in two chemical series, such as 4f block names as lanthanides or rare earth elements and 5f block names as actinides or actinides. In chemistry, the first inner transition metals series is made up of 4f-block elements or lanthanides, while the second inner transition metals series is made up of actinides.
Filling electrons in deep-seated 4f and 5f orbitals with increasing atomic number has resulted in the electronic configuration of the f-block chemical elements (lanthanum and actinium). All f-block elements have a trivalent oxidation number or state, which is a stable or common oxidation state.
Definition of f Block elements
The elements in which the last electron enters any of the seven f-orbitals of their respective ante-penultimate shells are referred to as F-Block elements. These elements have the electrons (1 to 14) in the f orbital and (0 to 1) in the penultimate energy level’s d orbital, and (0 to 1) in the outermost orbital. In the f-block, there are primarily two series that correspond to the filling of 4f and 5f orbitals.
The elements are divided into two groups: the 4f series of Ce to Lu and the 5f series of Th to Lw. Each series contains 14 elements that fill the ‘f’ orbital.
Classification of the Elements of f-Block
The two series of f-block elements or inner transition elements are lanthanides and actinides.
- Lanthanide series: The lanthanides are the first series of elements, which include elements with atomic numbers ranging from 57 to 71. These are non-radioactive elements (except for promethium). The last electron in the lanthanide series enters the 4f orbital.
- Actinide series: The actinide series consists of elements with atomic numbers ranging from 89 to 103. In general, these elements are radioactive in nature. The final electron in the actinide series enters the 5f orbital.
Periodic Table of Elements F-Block
The F-Block elements are traditionally found on the Periodic Table in two separate horizontal rows that are disjointed and located at the bottom of the table. Because of the space on the Periodic Table from which they are removed, the F-Block elements are often referred to as “inner transition metals.”
If these elements could fit inside the table, they would be in the transition metal section of the Periodic Table, between groups 2 and 3. They were removed in order for the entire table to fit together more cohesively. By separating those two periods, elements in the remainder of the table align with other elements with similar properties.
Properties of f-Block elements
Lanthanides, for example, are f-block chemical elements that behave as active metals. As a result, their redox reaction potential is comparable to that of alkaline earth metals. All f-block metals are strong reducing agents, and chemical reactions with acids result in the release of hydrogen ions.
As a result, they absorb hydrogen ions from low pH scale solutions, resulting in the formation of interstitial hydrides. Although there are significant similarities between the two series of f-block elements, there are also significant differences. These differences occur because 5f block elements have lower bond energies, ionisation energies, and less effective shielding electrons than 4f-block elements. With increasing atomic number, the standard electrode potentials for f-block lanthanides become more positive. However, for actinium, electrode potential values increase from actinium to uranium and then decrease until Americium.
Periodic Table of Lanthanides
The periodic table’s 4f block elements have been variously referred to as rare earth, lanthanum.
The name rare-earth has been given to f-block because it was originally extracted from oxides with the ancient name earth and are considered to be rare in the earth environment. The term rare earths is no longer used because many of these elements are no longer rare but rather abundant.
f-orbital
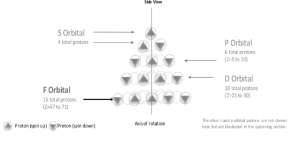
The f block sequence is one-of-a-kind. It begins with lanthanum (Z=57) and progresses through a 15-element block. A tetrahedron’s fifth level has 15 units. The f block has 15 elements (Z=57 to 71), but an odd number affects the number of orbitals (14 / 2 = 7).
To compensate, it converts a proton to a neutron in the next d block, beginning with the 5d block.
Conclusion
The elements in which the last electron enters any of the seven f-orbitals of their respective ante-penultimate shells are referred to as F-Block elements. In the periodic table, f block elements appear in two chemical series, such as 4f block names as lanthanides or rare earth elements and 5f block names as actinides or actinides. The elements in which the last electron enters any of the seven f-orbitals of their respective ante-penultimate shells are referred to as F-Block elements. These elements have the electrons in the f orbital and in the penultimate energy level d orbital, and in the outermost orbital. In the f-block, there are primarily two series that correspond to the filling of 4f and 5f orbitals. The elements are divided into two groups: the 4f series of Ce to Lu and the 5f series of Th to Lw.
 Profile
Profile Settings
Settings Refer your friends
Refer your friends Sign out
Sign out




